Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna: Gain & Axial Ratio Tips
When satellite ground stations lose critical signal lock during severe weather conditions or defense radar systems struggle with target discrimination, the root cause often traces back to inadequate antenna performance, specifically poor axial ratio and insufficient gain characteristics. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna addresses these critical challenges by delivering superior polarization purity and consistent gain performance across wide frequency ranges, ensuring reliable communication links even in the most demanding operational environments where signal integrity cannot be compromised.
Understanding Gain Performance in Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antennas
Antenna gain represents one of the most fundamental performance metrics that directly impacts transmission range and signal strength capabilities in modern communication systems. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna achieves gain values typically ranging from 10 to 20 dBi depending on the specific model configuration and operating frequency band. This gain characteristic determines how effectively the antenna can concentrate electromagnetic energy in a desired direction, with higher gain values translating to improved signal-to-noise ratios and extended communication ranges. The conical geometry inherently contributes to gain enhancement through its carefully engineered flare angle, which optimizes the aperture efficiency while maintaining impedance matching across the operational bandwidth. Advanced Microwave Technologies manufactures Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna solutions with precisely controlled gain specifications, leveraging over 20 years of microwave engineering expertise to deliver consistent performance. The gain stability across the 1 GHz to 40 GHz frequency range ensures that these antennas maintain reliable operation whether deployed in satellite communications, aerospace applications, or defense systems requiring precise signal directionality.
Factors Affecting Antenna Gain Optimization
Multiple design parameters influence the achievable gain in Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna implementations, with aperture diameter serving as the primary determinant of maximum gain potential. The relationship between aperture size and gain follows well-established electromagnetic principles, where larger apertures enable higher directivity but must be balanced against physical constraints and beamwidth requirements. The flare angle of the conical section critically affects how electromagnetic waves transition from the waveguide feed to free space propagation, with optimal angles minimizing return loss while maximizing forward radiation efficiency. Material selection plays an equally important role, as surface conductivity directly impacts insertion loss and overall antenna efficiency. Advanced Microwave Technologies utilizes high-grade aluminum construction in their Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna products, providing excellent conductivity while maintaining reasonable weight characteristics for practical installations. The feed network design must also support uniform amplitude and phase distribution across the aperture to achieve theoretical gain limits. Engineers can enhance gain performance through corrugated sections or choke ring implementations that reduce sidelobe levels and improve pattern symmetry, though these additions increase manufacturing complexity and cost considerations.
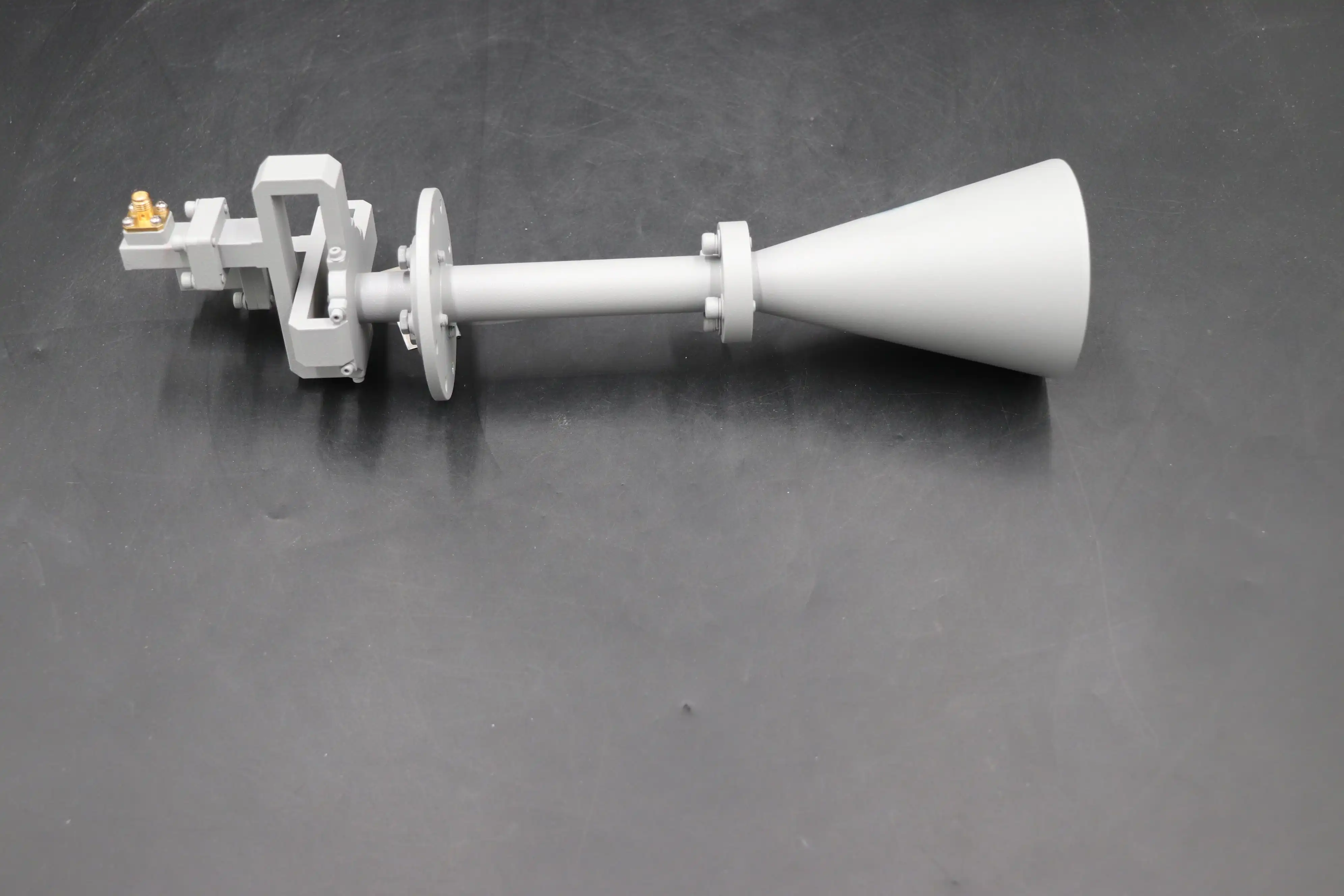
Achieving Optimal Axial Ratio in Circular Polarization Applications
The axial ratio parameter serves as the definitive measure of circular polarization quality, quantifying how closely the electromagnetic wave approximates perfect circular polarization characteristics. Measured in decibels, lower axial ratio values indicate superior polarization purity, with the industry standard threshold of 3 dB representing acceptable circular polarization performance across the antenna's operational bandwidth. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna achieves excellent axial ratio performance through carefully engineered feed structures that generate the precise 90-degree phase differential between orthogonal field components required for circular polarization generation. This phase relationship must remain stable across frequency and spatial dimensions to maintain polarization purity throughout the radiation pattern. Advanced implementations can achieve axial ratios below 1 dB at center frequency, degrading gradually toward band edges while remaining within the 3 dB specification across the entire operational bandwidth. The importance of tight axial ratio control becomes evident in satellite communications where polarization mismatch directly translates to signal loss, potentially dropping communication links during critical operations. Defense applications similarly demand stringent axial ratio specifications to minimize vulnerability to electronic countermeasures and ensure reliable target detection regardless of target polarization orientation.
Technical Approaches to Axial Ratio Improvement
Improving axial ratio performance in Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna designs requires sophisticated engineering approaches that address both feed network symmetry and aperture field distribution. The feed structure must generate two orthogonal modes with precisely controlled amplitude balance and phase quadrature, typically achieved through specialized polarizer designs integrated into the waveguide transition section. Dielectric plate polarizers offer one proven approach, utilizing anisotropic material properties to introduce differential phase shift between perpendicular polarization components while maintaining broadband operation. The geometric symmetry of the conical horn itself contributes significantly to axial ratio stability, as any asymmetries in the physical structure translate directly to polarization impurity through unbalanced field distributions. Manufacturing tolerances therefore become critical, with Advanced Microwave Technologies employing precision CNC machining capabilities in their 24-meter microwave darkroom facility to verify axial ratio performance across the full 0.5 to 110 GHz measurement capability range. Surface treatments and finish quality similarly impact high-frequency axial ratio performance by affecting boundary condition uniformity around the antenna circumference. Corrugated horn designs can further improve axial ratio bandwidth through their ability to equalize the propagation characteristics of different mode combinations, though at the cost of increased mechanical complexity. Designers must carefully balance axial ratio performance against other system requirements including gain, bandwidth, power handling, and physical size constraints when optimizing Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna configurations for specific applications.
Bandwidth Considerations for Wideband Operation
Operational bandwidth represents a critical specification for modern communication systems that must accommodate multiple frequency allocations or frequency-agile operation modes. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna excels in broadband applications through its inherent geometric properties that support wide impedance matching and polarization bandwidth. The conical flare angle enables gradual impedance transformation from the feed waveguide to free space, minimizing reflection losses across octave or multi-octave frequency ranges. Advanced designs achieve impressive bandwidth performance, with some implementations demonstrating greater than 60 percent impedance bandwidth while maintaining axial ratio specifications below 3 dB across similar frequency spans. This wideband capability proves essential in applications ranging from multi-band satellite ground stations that must receive signals across C, X, and Ku bands simultaneously, to electronic warfare systems requiring instantaneous frequency coverage for threat detection and analysis. The challenge in wideband Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna design lies in maintaining both impedance match and circular polarization characteristics across the entire operational spectrum, as different frequency components interact differently with the physical antenna structure. Advanced Microwave Technologies addresses these challenges through comprehensive electromagnetic simulation and optimization in their state-of-the-art 24-meter microwave darkroom, where antenna radiation patterns, gain, and impedance characteristics can be meticulously analyzed across the full frequency range to ensure specification compliance before delivery to customers.
Balancing Gain and Axial Ratio Across Frequency
The relationship between gain and axial ratio performance across operational bandwidth presents fundamental tradeoffs that antenna engineers must carefully navigate during the design optimization process. At lower frequencies where the antenna electrical size decreases, gain naturally reduces following the relationship between aperture size and operating wavelength, while polarization purity may improve due to reduced sensitivity to mechanical tolerances. Conversely, at higher frequencies where electrical size increases, gain improves but axial ratio can degrade if feed network phase balance deteriorates or if higher-order modes begin propagating in the feed structure. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna geometry offers advantages in managing these tradeoffs through its smooth impedance transformation and inherent mode filtering characteristics that suppress unwanted modes while supporting the desired circular polarization mechanism. Advanced Microwave Technologies engineers optimize this balance through iterative simulation and measurement, leveraging their Antenna Plane Near and Far Field Measuring Recombination Chamber to characterize both near-field and far-field behavior across the full operational spectrum. This comprehensive measurement capability enables verification that gain and axial ratio specifications meet requirements at all frequencies within the operational band, not just at discrete spot frequencies. Material selection contributes to bandwidth performance as well, with Advanced Microwave's aluminum construction providing stable electrical properties across temperature and frequency while maintaining the precise dimensional tolerances required for consistent performance. The result is Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna products that deliver reliable gain and axial ratio performance across their entire specified frequency range, meeting the demanding requirements of satellite communications, aerospace, defense, and navigation applications.

Practical Implementation and Testing Strategies
Successfully deploying Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna systems requires careful attention to installation practices, system integration considerations, and comprehensive testing protocols to verify performance specifications. The antenna mounting structure must provide rigid mechanical support while avoiding metallic surfaces in the near-field region that could disturb radiation patterns or degrade polarization purity through unwanted reflections. Feed network connections require precise alignment and secure attachment to maintain impedance matching and minimize insertion loss, with connector types including SMA and N-type options providing 50-ohm interface compatibility with standard RF equipment. Environmental protection becomes essential in outdoor installations, where Advanced Microwave's robust aluminum construction and optional environmental sealing protect against moisture, temperature extremes, and corrosive atmospheres that could degrade performance over time. Testing procedures should verify critical parameters including return loss across the operational bandwidth, ensuring VSWR remains below specified thresholds typically around 1.5:1 for quality antenna systems. Radiation pattern measurements in both principal planes confirm gain specifications and pattern symmetry while identifying any unwanted sidelobe or backlobe contributions that could compromise system performance. Axial ratio testing presents particular challenges, requiring specialized measurement equipment and procedures to accurately characterize polarization purity across both frequency and angular dimensions. Advanced Microwave Technologies provides comprehensive technical support throughout the implementation process, from initial specification development through installation assistance and post-deployment troubleshooting, leveraging their extensive experience across satellite communications, defense, aerospace, and navigation applications to ensure successful system integration.
Conclusion
Optimizing Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna performance requires balancing gain, axial ratio, and bandwidth specifications to meet application requirements across diverse operating conditions.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd. stands as your trusted China Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna manufacturer, China Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna supplier, and China Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna factory with over 20 years of proven excellence. We offer China Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna wholesale solutions with competitive Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna price points, delivering High Quality Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna products with Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna for sale backed by ISO certifications and comprehensive OEM services. Our perfect supply chain system, professional technical R&D team, and strict quality control ensure fast delivery of customized solutions from our state-of-the-art 24-meter microwave darkroom facility equipped with measurement capabilities up to 110 GHz. From prototyping through full production and technical support, our expert engineers provide guidance throughout your project lifecycle. Contact us at craig@admicrowave.com to discuss your specific requirements and experience the Advanced Microwave difference in satellite communications, aerospace, defense, and navigation applications worldwide.
References
1. Nguyen, D.D., and Kim, S., "Conical Horn Antenna with High Gain and Circular Polarization for Sub-mm-Wave/Terahertz," Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves
2. Wang, H., Zhang, Y., and Chen, L., "Broadband Circularly Polarized Conical Corrugated Horn Antenna Using a Dielectric Circular Polarizer," Micromachines
3. Cheng, X., Yao, Y., Yu, T., Chen, Z., Yu, J., and Chen, X., "Analysis and Design of a Low-Cost Circularly Polarized Horn Antenna," IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation
4. Lin, C., Ge, Y., Bird, T.S., and Liu, K., "Circularly Polarized Horns Based on Standard Horns and a Metasurface Polarizer," IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters
5. Shi, H.Y., Li, A.X., Zhang, J.Q., and Wang, J., "Design of a Circular Polarized Horn Antenna with an Anisotropic Metamaterial Slab," Progress in Electromagnetics Research












