Low-Reflection Coaxial Load Designs: What Matters Most?
Picture this: your high-power radar system suddenly displays erratic readings, your satellite ground station loses critical communication links, or your RF testing equipment produces unreliable measurements. The culprit? Reflected signals bouncing back through your coaxial load, creating standing waves that wreak havoc on your entire system. In RF and microwave systems operating from DC to 110 GHz, achieving minimal reflection in coaxial load designs isn't just about performance optimization—it's about preventing equipment damage, ensuring measurement accuracy, and maintaining system stability. The difference between a well-designed low-reflection coaxial load and a mediocre one can mean the distinction between flawless operation and catastrophic failure in defense radar systems, aerospace communications, or precision laboratory measurements.
Understanding Impedance Matching in Coaxial Load Systems
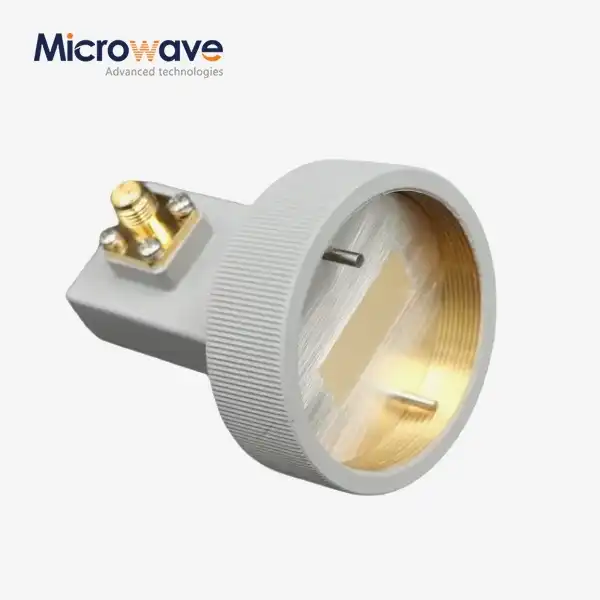
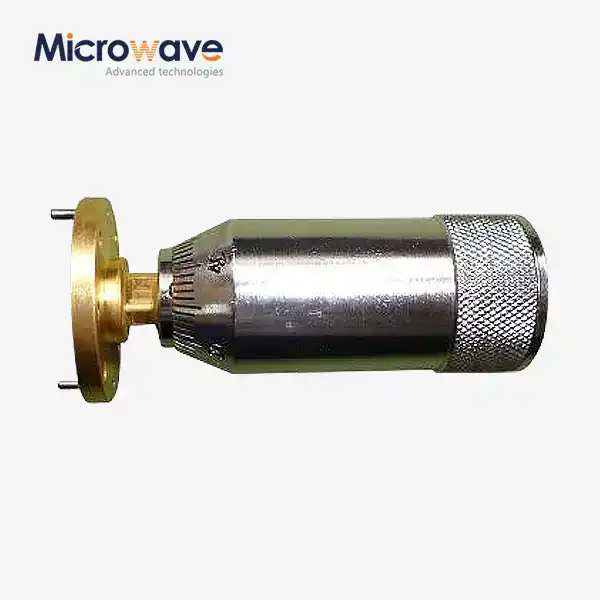
The foundation of any low-reflection coaxial load design rests on achieving precise impedance matching between the transmission line and the terminating load. When a coaxial transmission line encounters a load with impedance that differs from its characteristic impedance—typically 50 ohms in most RF systems—a portion of the incident signal reflects back toward the source rather than being absorbed. This reflection phenomenon creates standing waves along the transmission line, which not only degrades signal quality but can also damage sensitive components when dealing with high-power applications. The voltage standing wave ratio serves as the primary metric for quantifying reflection performance, with lower VSWR values indicating superior impedance matching and minimal signal reflection. Advanced Microwave's CL series coaxial load achieves exceptional impedance matching through precision engineering that maintains VSWR below 1.2:1 across the entire operational frequency range from DC to 110 GHz. This remarkable performance stems from careful selection of resistive materials and meticulous control of dimensional tolerances during manufacturing. The resistive element within the coaxial load must present a purely resistive impedance at the operating frequency, free from reactive components that would compromise matching performance. Modern coaxial load designs employ specialized resistive films or bulk resistive materials whose electrical properties remain stable across temperature variations and power levels, ensuring consistent impedance matching throughout diverse operating conditions.

Critical Design Parameters for Minimal Reflection
Several interconnected design parameters determine the reflection characteristics of coaxial load terminations. The physical geometry of the resistive element plays a crucial role—a gradual taper from the connector interface to the resistive section minimizes abrupt impedance discontinuities that would otherwise generate reflections. The length and profile of this transition region must be optimized for the specific frequency range of operation, with higher frequencies requiring more carefully controlled transitions due to shorter wavelengths. Material selection for the resistive element represents another critical consideration, as the resistivity, temperature coefficient, and frequency-dependent behavior directly impact both impedance matching and power handling capability. Connector interface quality constitutes a frequently overlooked yet vital aspect of low-reflection design. Even with an ideally matched resistive termination, poor connector quality or improper mating can introduce significant reflections at the interface between the coaxial load and the transmission line. Advanced Microwave Technologies addresses this challenge by offering coaxial loads with multiple connector types including SMA, N-Type, TNC, and 2.92mm configurations, all manufactured to exacting tolerances that ensure reliable, repeatable connections with minimal interface reflections. The connector center pin alignment, outer conductor contact pressure, and dielectric support positioning all influence the overall reflection performance of the assembled system.
Thermal Management Impact on Reflection Characteristics
Thermal considerations profoundly influence the reflection performance of coaxial load designs, particularly in high-power applications where significant heat generation occurs. As the resistive element absorbs RF energy and converts it to heat, temperature rise within the component can alter material properties and consequently affect impedance matching. Quality coaxial load designs incorporate thermal management strategies that maintain the resistive element within its optimal temperature range, preserving stable electrical characteristics even under sustained high-power operation. Advanced heat dissipation materials integrated into the load structure facilitate efficient thermal conduction away from the resistive element, preventing localized hot spots that could compromise both performance and reliability. The relationship between power handling and reflection performance creates a delicate balance in coaxial load design. Higher power dissipation generates greater thermal stress on materials, potentially leading to temperature-dependent impedance variations that manifest as increased VSWR at elevated power levels. Advanced Microwave's coaxial loads address this challenge through sophisticated thermal engineering that enables power handling up to 500 Watts while maintaining consistent low-reflection performance throughout the power range. The thermal design must account for both steady-state power dissipation and transient thermal response, ensuring that the load can accommodate pulsed RF signals without experiencing thermal-induced reflection spikes during power transitions.
Material Science in Low-Reflection Design
Material selection represents perhaps the most fundamental determinant of coaxial load reflection performance. The resistive material must exhibit several critical properties simultaneously: appropriate resistivity to achieve 50-ohm impedance, low temperature coefficient to minimize thermal drift, stable frequency response across the operational bandwidth, and sufficient power handling capacity to withstand the thermal stresses of RF energy absorption. Traditional thin-film resistive materials offer excellent high-frequency performance but may have limited power handling, while bulk resistive ceramics provide robust power capacity but can present challenges in achieving uniform impedance across wide frequency ranges. Modern coaxial load designs often employ composite material systems that combine the advantages of different material types. A common approach utilizes a bulk resistive core for high power handling, surrounded by precision thin-film elements that fine-tune the impedance matching at specific frequencies. The dielectric materials supporting the resistive elements must also be carefully selected, as their loss tangent and dielectric constant influence the overall electromagnetic behavior of the load. Advanced Microwave Technologies manufactures coaxial loads using cutting-edge CNC machining techniques that ensure exceptional accuracy in material placement and dimensional control, both critical factors in achieving the tight tolerances necessary for minimal reflection across broad frequency ranges.
Frequency-Dependent Behavior and Broadband Performance
Achieving low reflection across wide frequency ranges presents substantially greater design challenges than optimizing performance at a single frequency. As frequency increases, wavelength decreases, making the physical dimensions of components increasingly significant relative to signal characteristics. A coaxial load design optimized for VHF frequencies may exhibit unacceptable reflections when used at microwave frequencies, as dimensional tolerances that were negligible at lower frequencies become major sources of impedance mismatch at higher frequencies. The transition from the connector to the resistive element becomes particularly critical at higher frequencies, where even minor discontinuities in diameter or dielectric properties can generate substantial reflections. Advanced Microwave's coaxial load products demonstrate exceptional broadband performance by incorporating frequency-compensated design elements that maintain low VSWR from DC through 110 GHz. This remarkable bandwidth coverage requires sophisticated electromagnetic modeling during the design phase, analyzing how different structural features influence reflection characteristics across the entire frequency range. The resistive element geometry, dielectric support structures, and connector interface must all be optimized simultaneously to achieve the desired broadband performance. At millimeter-wave frequencies approaching 110 GHz, manufacturing precision becomes paramount, as surface roughness and dimensional variations measured in micrometers can significantly impact reflection performance.
Measurement and Verification of Reflection Performance
Accurate characterization of coaxial load reflection performance requires specialized measurement equipment and techniques. Network analyzers capable of measuring S-parameters provide the most comprehensive assessment, revealing both the magnitude and phase of reflected signals across the frequency range of interest. The S11 parameter specifically quantifies the reflection coefficient, from which VSWR can be calculated. Advanced Microwave Technologies employs state-of-the-art measurement equipment in their laboratories, with capabilities extending to 110 GHz, ensuring that every coaxial load meets stringent quality standards before shipment. The 24m Microwave Darkroom facility enables far-field antenna measurements, while precision vector network analyzers verify component-level reflection characteristics. Measurement accuracy at millimeter-wave frequencies demands meticulous attention to calibration procedures and measurement uncertainties. Connector repeatability becomes a significant source of measurement variation, as even properly torqued connectors can exhibit slight variations in reflection performance with repeated connections. Quality manufacturers implement comprehensive testing protocols that account for these variations, often measuring multiple connection cycles to ensure consistent performance. Temperature-dependent measurements verify that the coaxial load maintains acceptable reflection characteristics across its rated operating temperature range of -55°C to +125°C, confirming that thermal effects do not compromise impedance matching under environmental extremes.
Application-Specific Design Considerations
Different applications impose distinct requirements on coaxial load reflection performance, necessitating tailored design approaches. In communications base stations, coaxial loads serve critical functions in power splitting networks and antenna testing, where precise impedance matching ensures signal integrity throughout the RF chain. Defense radar systems demand coaxial loads capable of absorbing high peak powers while maintaining low reflection to prevent false target returns generated by standing waves. Aerospace satellite communication systems require loads that can withstand extreme temperature cycling and vibration while delivering consistent low-reflection performance in the harsh space environment. Laboratory test and measurement applications represent perhaps the most demanding context for low-reflection coaxial loads, as measurement accuracy directly depends on minimizing reflections that could corrupt measured data. When characterizing amplifiers, filters, or other RF components, any reflection from the measurement system's terminating loads propagates through the device under test, creating measurement errors that obscure the true device performance. Advanced Microwave's coaxial loads find extensive use in these precision measurement scenarios, where their low VSWR specification ensures measurement integrity. Broadcasting infrastructure relies on high-power coaxial loads for transmitter testing and dummy load applications, where the ability to safely dissipate hundreds of watts while maintaining stable impedance protects expensive transmission equipment during maintenance and troubleshooting operations.
Conclusion
Low-reflection coaxial load design demands sophisticated integration of impedance matching, thermal management, material science, and precision manufacturing to achieve reliable performance across demanding applications from defense systems to laboratory measurements.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd brings over 20 years of microwave expertise to every coaxial load we manufacture, combining ISO 9001:2015 certified quality control with cutting-edge facilities including our 24m Microwave Darkroom for comprehensive testing. As a leading China Coaxial Load manufacturer, China Coaxial Load supplier, and China Coaxial Load factory, we offer High Quality Coaxial Load solutions with competitive Coaxial Load price points and Coaxial Load for sale globally through our China Coaxial Load wholesale programs. Our comprehensive OEM services provide customized power ratings, frequency ranges, and connector configurations tailored to your exact specifications, backed by our experienced technical team and rapid prototyping capabilities. Don't let inferior components compromise your system performance—contact our engineering team at craig@admicrowave.com today to discuss your coaxial load requirements and discover how our precision-engineered solutions can elevate your RF system reliability and performance.
References
1. Pozar, David M. "Microwave Engineering" Fourth Edition. John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
2. Rizzi, Peter A. "Microwave Engineering: Passive Circuits" Prentice Hall, 1988.
3. Ludwig, Reinhold and Gene Bogdanov. "RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications" Second Edition. Pearson Education, 2009.
4. Collin, Robert E. "Foundations for Microwave Engineering" Second Edition. IEEE Press, 2001.
5. Bahl, Inder J. "Lumped Elements for RF and Microwave Circuits" Artech House, 2003.












