Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna vs Linear Horn Antenna
When satellite ground stations experience signal degradation during atmospheric disturbances or when radar systems struggle with target detection in complex environments, the choice between a Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna and a linear horn antenna becomes mission-critical. Understanding the fundamental differences between these two antenna technologies is essential for engineers and system designers who need reliable, high-performance microwave communication solutions. This comprehensive comparison explores how circular polarization capabilities fundamentally transform signal integrity, examining performance characteristics, application scenarios, and technical considerations that determine which antenna type delivers optimal results for your specific requirements.
Understanding Polarization Fundamentals in Horn Antennas
The electromagnetic field behavior in horn antennas fundamentally depends on how the electric field vector propagates through space. In linear horn antennas, the electric field oscillates along a fixed axis, maintaining a constant orientation throughout signal transmission. This straightforward approach works well for many applications but presents limitations when signals encounter atmospheric effects, multipath interference, or when receiving antenna orientation cannot be precisely controlled. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna addresses these challenges through a fundamentally different electromagnetic approach where the electric field vector rotates in a circular pattern as the wave propagates, creating either right-hand circular polarization or left-hand circular polarization depending on the rotation direction. This rotational characteristic of the Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna provides inherent immunity to orientation misalignment between transmitting and receiving systems. When linearly polarized signals reflect off surfaces or pass through the ionosphere, their polarization angle can shift unpredictably, causing signal loss in systems using linear horn antennas. Circular polarization maintains signal integrity regardless of these rotational effects because the receiving antenna captures the signal energy regardless of how the polarization plane has shifted during transmission. This fundamental advantage makes the Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna indispensable for satellite communications, where signals traverse vast distances through varying atmospheric conditions and encounter Faraday rotation effects that would severely degrade linearly polarized transmissions.
The transition from linear to circular polarization requires sophisticated feed structures within the antenna design. Linear horn antennas achieve their polarization through straightforward waveguide coupling, where the rectangular or circular waveguide maintains the electric field orientation established at the input. In contrast, the Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna incorporates specialized feeding arrangements such as septum polarizers, dielectric-loaded plates positioned at precise angles, or quadrature hybrid couplers that generate the necessary phase differential between orthogonal field components. These feed mechanisms create the 90-degree phase shift between two perpendicular electric field components, resulting in the circular rotation pattern characteristic of circular polarization. Advanced Microwave Technologies manufactures high-quality circular polarization horn antennae that implement these sophisticated feed structures across different frequencies, different bandwidths, and gain requirements, providing electromagnetic vibrators that can be configured as circular polarization antennas, spiral antennas, circular polarization horn antenna apertures, microstrip circularly polarized antennas, reflector circular polarization antennas, variable polarization antennas, and other circular polarization antenna configurations.
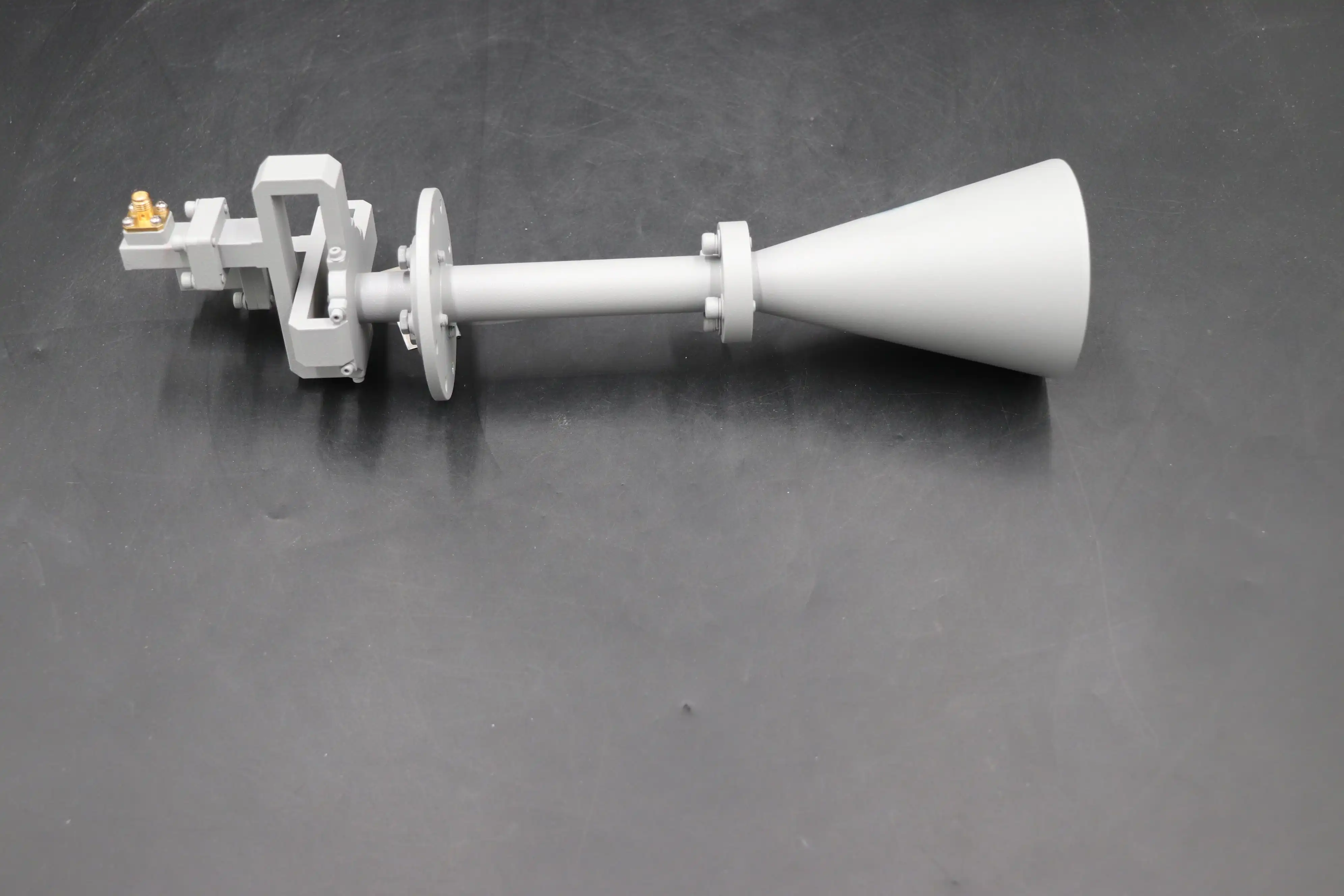
Technical Performance Comparison
Performance metrics reveal substantial differences between Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna systems and their linear counterparts. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna typically operates across frequency ranges from 1 GHz to 40 GHz with antenna gains between 10 to 20 dBi, though extended designs achieve higher directivity through optimized aperture dimensions and axial length configurations. These antennas maintain stable impedance characteristics at 50 Ohms with excellent VSWR performance, typically below 1.15:1 across operational bandwidths. Linear horn antennas achieve comparable gain figures through their pyramidal or conical geometries, but their performance degrades significantly when polarization orientation deviates from the optimal alignment angle. Cross-polarization discrimination represents another critical performance differentiator. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna maintains superior isolation between orthogonal polarization components, typically exceeding 25 dB separation across operational frequencies. This isolation ensures that signals maintain their intended polarization state without coupling energy into the opposite polarization sense. Linear horn antennas demonstrate excellent cross-polarization performance when properly aligned, but their discrimination characteristics depend heavily on mechanical precision in mounting and orientation. Manufacturing tolerances become more critical for linear designs because even slight misalignments introduce cross-polarization components that degrade overall system performance.
Bandwidth characteristics further distinguish these antenna technologies. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna provides exceptional frequency agility, accommodating various satellite service bands including L-band, S-band, C-band, X-band, Ku-band, K-band, and Ka-band operations without requiring antenna substitution. The conical geometry creates controlled impedance transformation that maintains consistent performance across wide frequency ranges. Linear horn antennas offer similar wideband capabilities in their native polarization, but systems requiring polarization flexibility must implement external polarization networks or multiple antenna elements. This architectural difference translates directly into system complexity, cost considerations, and maintenance requirements over operational lifetimes.
Application-Specific Performance Advantages
Satellite communication systems represent the primary domain where Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna technology demonstrates overwhelming advantages over linear alternatives. Earth-to-space communication links must traverse the ionosphere, where free electrons cause Faraday rotation that continuously changes the polarization plane of linearly polarized signals. This rotation varies with time of day, solar activity, and signal frequency, making reliable communication with linear horn antennas extremely challenging without active polarization tracking systems. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna eliminates this problem entirely because circular polarization remains unaffected by Faraday rotation magnitude. The signal maintains its circular polarization sense regardless of how many rotations the polarization plane undergoes during atmospheric transit. For satellite ground station applications, the Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna delivers consistent gain patterns across extended frequency ranges, enabling multi-band operation that supports diverse communication protocols simultaneously. Advanced Microwave's Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna designs provide reliable signal transmission for high-definition video downlinks, telemetry data channels, and voice communications without the complexity of motorized polarization adjustment mechanisms. The frequency coverage spanning 1 GHz to 40 GHz accommodates legacy satellite systems still operating at lower frequencies while supporting modern high-throughput satellites utilizing higher frequency allocations. This versatility reduces ground station infrastructure costs by eliminating the need for multiple antenna systems dedicated to specific frequency bands.
Radar and defense applications benefit from distinct advantages that the Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna provides for target detection and tracking scenarios. Circular polarization characteristics enhance target discrimination capabilities, particularly when detecting objects with complex geometries that present varying radar cross-sections under different polarization illuminations. Weather radar systems leverage these properties to distinguish between spherical raindrops and non-spherical ice crystals or debris, significantly improving precipitation classification accuracy and severe weather detection reliability. Military surveillance radars implement Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna technology to reduce susceptibility to jamming techniques and electronic countermeasures that typically exploit polarization characteristics of linearly polarized systems.
Manufacturing and Customization Considerations
The manufacturing complexity differs significantly between Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna designs and linear horn configurations. Linear horn antennas benefit from straightforward fabrication processes, particularly for pyramidal designs where rectangular waveguide interfaces and flared apertures can be produced using conventional machining techniques. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna requires additional manufacturing steps to incorporate the polarization-generating feed structures. Septum polarizers demand precise machining tolerances to achieve the quarter-wave transformation necessary for proper circular polarization generation. Dielectric-loaded plates must be fabricated from materials like PTFE with specific dielectric constants and positioned at exact angles to introduce the required 45-degree phase shift between field components. Advanced Microwave Technologies addresses these manufacturing challenges through sophisticated fabrication capabilities backed by over 20 years of experience in microwave products. Our production facilities employ precision metal turning operations optimized for circular cross-sections, ensuring the geometric accuracy essential for Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna performance. Interior surface finish receives particular attention because wall roughness directly impacts electrical performance, especially at higher microwave frequencies where skin depth effects concentrate currents near conductor surfaces. Our quality control procedures verify that each Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna meets stringent specifications for axial ratio, cross-polarization isolation, and return loss across the full operating bandwidth before delivery to customers.
Customization flexibility represents a significant consideration when selecting between antenna technologies. The Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna offers extensive customization options including frequency range adjustments, aperture size modifications, material selection for specific environmental conditions, and connector type variations to match existing system interfaces. Advanced Microwave provides tailored OEM services for the Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna, working closely with engineering teams to optimize antenna parameters for specific application requirements. Whether adjusting the polarization sense from right-hand to left-hand circular polarization, modifying power handling capabilities from the standard 50 watts continuous rating, or implementing specialized mounting configurations, our technical staff delivers comprehensive support throughout the design and integration process.
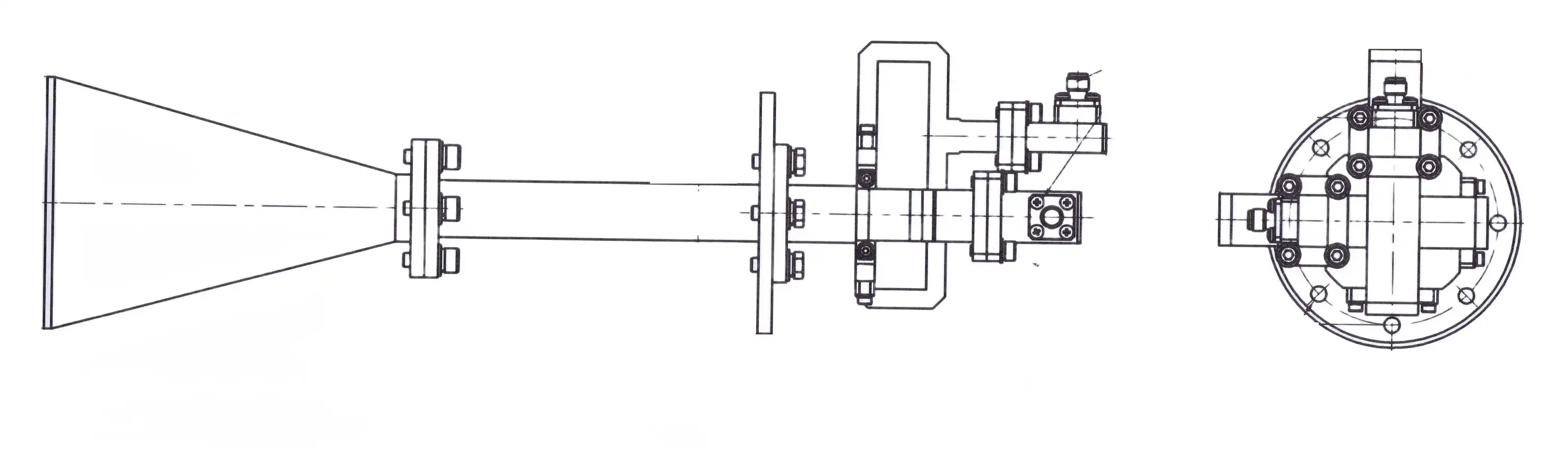
System Integration and Performance Optimization
Successful implementation of Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna systems requires careful attention to feed network design and impedance matching throughout the signal chain. The antenna typically interfaces through SMA or N-type connectors depending on frequency range and power handling requirements. Proper connector selection and installation prevent standing wave problems that degrade efficiency and potentially damage components under high-power transmission conditions. For receiving applications, positioning low-noise amplifiers as close as possible to the Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna minimizes cable losses that would otherwise reduce system sensitivity in weak signal scenarios. The 50-ohm impedance standard facilitates integration with commercial microwave components, but verification through return loss measurements ensures proper matching across operational frequencies. Calibration procedures validate that the Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna delivers specified performance in actual deployment conditions. Axial ratio measurements confirm circular polarization quality, with values approaching unity indicating ideal circular polarization where the two orthogonal field components maintain equal magnitude and precise 90-degree phase relationship. Specialized test equipment including vector network analyzers with polarization analysis capabilities enable comprehensive characterization of radiation patterns, cross-polarization discrimination, and impedance characteristics. These measurements identify potential installation issues such as blockage from nearby structures, ground plane effects that distort patterns, or feed network problems that compromise polarization purity.
Environmental factors influence Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna performance in ways that differ from linear horn antenna behavior. Temperature variations affect the dielectric properties of polarization-generating structures within the feed network, potentially shifting the phase relationship between orthogonal components and degrading axial ratio performance. Advanced Microwave's Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna designs incorporate temperature-stable materials and compensation techniques that maintain polarization purity across operational temperature ranges. The robust aluminum construction provides mechanical stability under wind loading while ensuring thermal expansion characteristics remain compatible with precision electrical requirements. Customizable material options address specific environmental challenges such as corrosive marine atmospheres or extreme temperature cycling in aerospace applications.
Conclusion
Selecting between Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna and linear horn antenna technologies requires careful evaluation of application requirements, atmospheric conditions, and system architecture constraints for optimal microwave communication performance.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd. (ADM) brings over 20 years of specialized expertise as a leading China Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna manufacturer, China Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna supplier, and China Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna factory serving global markets. Our comprehensive product portfolio includes High Quality Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna systems, waveguide assemblies, coaxial components, and feed networks precisely engineered for satellite communications, defense, aerospace, and navigation applications. With our state-of-the-art 24m Microwave Darkroom and measurement capabilities extending to 110 GHz, we deliver ISO-certified solutions backed by rigorous testing protocols. Whether you need China Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna wholesale volumes, Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna for sale in custom configurations, or competitive Conical Circular Polarization Horn Antenna price quotations, our technical team provides rapid prototyping, comprehensive OEM services, and expert guidance for seamless system integration. Contact craig@admicrowave.com today to discuss your requirements and discover how our proven supply chain, advanced R&D capabilities, and exceptional after-sales support deliver the antenna solutions your critical applications demand.
References
1. Bozzi, M., Georgiadis, A., and Wu, K. "Review of Substrate-Integrated Waveguide Circuits and Antennas." IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, Institute of Engineering and Technology.
2. Balanis, C. A. "Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design." John Wiley & Sons, Fourth Edition.
3. Rudge, A. W., Milne, K., Olver, A. D., and Knight, P. "The Handbook of Antenna Design." Peter Peregrinus Ltd, Volumes 1 and 2.
4. Olver, A. D., Clarricoats, P. J. B., Kishk, A. A., and Shafai, L. "Microwave Horns and Feeds." IEEE Press and IET Electromagnetic Waves Series.
5. Milligan, T. A. "Modern Antenna Design." John Wiley & Sons, Second Edition.












