Why Every Test Lab Needs an Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe?
Picture this scenario: your test lab receives a critical phased array antenna for 5G deployment. The far-field distance requires 30 meters of clearance, but your facility only has 10 meters. Traditional testing is impossible, deadlines are looming, and equipment rental costs are skyrocketing. This is where an Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe becomes indispensable. By enabling precise electromagnetic field characterization at reduced distances, these probes solve the fundamental challenge test labs face: achieving accurate antenna measurements without requiring massive anechoic chambers or outdoor test ranges. For any laboratory conducting antenna development, quality control, or compliance testing, near-field measurement capabilities represent the difference between operational flexibility and costly limitations.
Understanding Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe Technology
The Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe represents a paradigm shift in how modern test laboratories characterize antenna performance. Unlike traditional far-field testing that demands distances calculated by the formula 2D²/λ (where D represents the antenna's largest dimension and λ is wavelength), near-field measurement technology operates within just a few wavelengths from the antenna under test. This proximity advantage fundamentally transforms laboratory requirements and measurement possibilities. The probe functions as a sophisticated sensor that captures both amplitude and phase information of the electromagnetic field surrounding an antenna, collecting granular data that mathematical algorithms then transform into far-field radiation patterns through Fourier transforms and spherical wave expansion techniques. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd offers Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe solutions spanning frequencies from 10 MHz to 110 GHz, accommodating everything from legacy communication systems to cutting-edge millimeter-wave applications. These probes are engineered with high-durability composite materials and feature multiple operational modes including electric field sensing, magnetic field detection, and dual-mode capabilities. The measurement accuracy of ±0.5% ensures that even minute variations in electromagnetic field distribution are captured reliably, which proves critical when optimizing antenna designs for satellite communications, aerospace radar systems, defense applications, and next-generation telecommunications infrastructure. The versatility of these measurement systems makes them essential equipment across planar near-field, cylindrical near-field, spherical near-field, and time-domain near-field measurement configurations.
The Physics Behind Near Field Measurement
Understanding the electromagnetic theory underlying near-field measurements illuminates why these probes deliver such valuable data. In the region immediately surrounding an antenna, electromagnetic fields exhibit complex reactive and radiating components that haven't yet settled into the simple plane-wave characteristics observed in the far-field region. An Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe operating in this zone captures the intricate field structure, measuring both the magnitude and phase relationships that define how energy propagates from the antenna aperture. The probe's positioning system must achieve exceptional accuracy, typically within λ/50 to λ/100 tolerances, because even millimeter-level deviations at high frequencies can introduce significant phase errors that corrupt measurement results. The mathematical transformation from near-field data to far-field radiation patterns relies on electromagnetic reciprocity principles and modal expansion theory. When a probe scans across a measurement plane collecting complex field data at properly spaced grid points, this information contains all necessary details about the antenna's radiation characteristics. Advanced signal processing algorithms decompose the measured fields into spherical wave modes, apply probe correction factors accounting for the probe's own radiation pattern, and synthesize the far-field pattern that would be observed at infinite distance. This computational approach not only eliminates the need for enormous test facilities but actually provides more comprehensive data than conventional far-field measurements, capturing detailed information about antenna aperture field distributions that direct far-field testing cannot reveal.
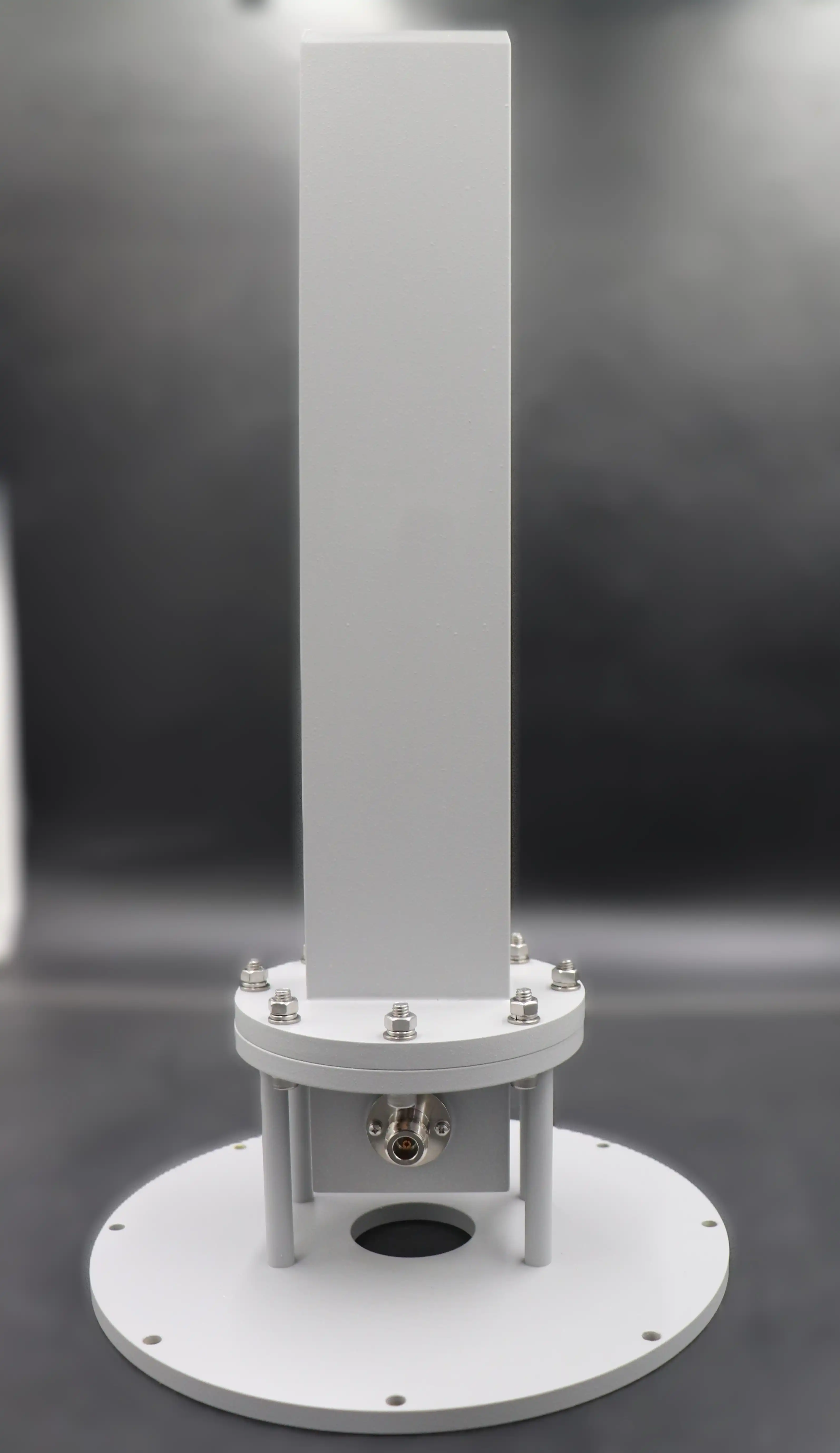
Key Advantages for Modern Test Laboratories
Test laboratories equipped with Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe capabilities gain multiple strategic advantages that directly impact operational efficiency and measurement quality. First, the dramatically reduced space requirements mean that comprehensive antenna characterization can occur within compact anechoic chambers measuring just several meters across, rather than requiring outdoor test ranges or massive indoor facilities spanning tens of meters. This space economy translates directly into reduced facility costs, climate-controlled testing environments that eliminate weather dependencies, and the ability to establish antenna test capabilities in locations where far-field ranges would be impractical or impossible. Second, near-field measurement systems deliver significantly faster data acquisition compared to far-field approaches. While traditional far-field pattern measurements require rotating the antenna through hundreds of angular positions and recording data at each point, near-field scanning collects data across a two-dimensional plane in a single automated sequence. The measurement speed advantage becomes even more pronounced when characterizing antennas with complex radiation patterns or when conducting multiple frequency sweeps. Test labs can complete comprehensive antenna evaluations in hours rather than days, enabling rapid prototyping cycles and efficient production testing workflows. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd's pre-calibrated, traceable Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe systems with customizable dimensions ensure seamless integration into existing test infrastructure while maintaining ISO 9001:2008 compliance standards.
Critical Applications Driving Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe Adoption
Satellite Communications Testing Requirements
The satellite communications industry presents particularly demanding antenna testing challenges that make Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe technology practically indispensable. Satellite ground station antennas typically feature large apertures ranging from one to several meters in diameter, operating across frequency bands from L-band through Ka-band and beyond. Calculating the far-field distance for a two-meter Ka-band antenna yields measurement ranges exceeding 50 meters, requiring facility dimensions and environmental controls that most organizations find cost-prohibitive. Near-field measurement techniques solve this challenge by enabling complete antenna characterization within laboratory-scale facilities while maintaining measurement accuracy sufficient for critical satellite link budget calculations. Beyond practical space considerations, satellite antenna testing demands extremely precise sidelobe and cross-polarization measurements to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and prevent interference with adjacent satellite systems. An Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe captures the complete amplitude and phase distribution across the antenna aperture, enabling mathematical analysis that accurately predicts sidelobe levels, beam pointing accuracy, and polarization purity across the entire operational frequency range. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd's measurement systems spanning up to 110 GHz support both current satellite communication bands and emerging high-frequency applications, while the customizable probe configurations accommodate diverse antenna geometries from circular reflectors to shaped-beam arrays. The high measurement accuracy ensures that antenna manufacturers can verify performance specifications with confidence before expensive deployment to ground stations or integration into spacecraft platforms.
Aerospace and Defense Radar System Development
Aerospace and defense radar systems represent another critical application domain where Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe technology proves essential. Modern radar antennas increasingly employ sophisticated phased array architectures with hundreds or thousands of individual elements, each requiring precise amplitude and phase control to achieve desired beam steering and null placement capabilities. Testing these complex systems demands measurement techniques capable of characterizing not just the overall antenna pattern but also the performance of individual array elements and the feed network distribution accuracy. Near-field measurement approaches excel at this detailed diagnostic work, providing spatial field distribution maps that reveal fabrication defects, element failures, or feed network imbalances that would be extremely difficult to identify through far-field testing alone. Military radar applications often involve antennas optimized for specific detection and tracking scenarios, with carefully engineered sidelobe structures, monopulse tracking capabilities, and adaptive nulling features. Validating these sophisticated performance characteristics requires measurement systems offering exceptional dynamic range and phase measurement precision. An Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe operating across wide frequency ranges with multiple probe type options enables comprehensive characterization of X-band fire control radars, surveillance systems operating across multiple frequency bands, and millimeter-wave radar seekers for precision-guided munitions. The controlled laboratory environment possible with near-field testing also facilitates secure testing of classified antenna designs without the operational security challenges associated with outdoor far-field ranges. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd's experience supporting defense contractors through their 24m Microwave Darkroom and advanced measurement capabilities up to 110 GHz positions them as a trusted partner for sensitive military antenna development programs.
Implementing Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe Systems
Essential System Components and Configuration
Establishing an effective near-field measurement capability requires integrating several key system components beyond the Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe itself. The mechanical positioning system forms the foundation, providing the precision motion control necessary to scan the probe across the measurement plane with submillimeter accuracy. Planar near-field systems typically employ XY scanner assemblies with linear positioning stages, while cylindrical and spherical configurations add rotational axes to position either the antenna under test or the probe through the required measurement trajectory. The positioning system's mechanical stability and repeatability directly impact measurement quality, making robust engineering and calibration essential considerations. The radio frequency measurement instrumentation must support complex signal measurements, capturing both amplitude and phase information at each scan position. Vector network analyzers represent the most common measurement approach, providing calibrated magnitude and phase data across wide frequency ranges with excellent dynamic range and measurement speed. The system requires careful RF cable management to minimize phase variations as the probe moves through its scanning trajectory, often employing precision phase-stable cables or implementing cable flexure compensation algorithms. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd supplies Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe systems with appropriate SMA or N-Type connectors matched to standard RF measurement equipment, simplifying integration while ensuring signal integrity throughout the measurement chain. The probe selection itself demands attention to factors including frequency range coverage, polarization measurement requirements, and spatial resolution needs, with options ranging from simple open-ended waveguides to sophisticated dual-polarized probe designs offering simultaneous orthogonal polarization measurements.
Data Processing and Analysis Workflows
The raw data collected during near-field scanning represents just the starting point for antenna characterization. Sophisticated data processing workflows transform the measured near-field distribution into meaningful antenna performance metrics through multiple computational stages. Initial data processing typically includes probe position error correction, cable flexure compensation, and drift correction to account for any instrumentation variations occurring during the measurement sequence. The core near-field to far-field transformation then applies fast Fourier transform algorithms or spherical mode expansion techniques, implementing probe correction factors that account for the probe's own radiation characteristics and effectively deconvolve the probe's influence from the measurement results. The processed far-field patterns enable engineers to extract standard antenna performance parameters including gain, beamwidth, sidelobe levels, cross-polarization characteristics, and beam pointing accuracy. Advanced analysis can generate three-dimensional radiation pattern visualizations, compute antenna efficiency by integrating radiated power, and compare measured results against design specifications or simulation predictions. Many modern Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe systems include comprehensive software packages automating these analysis workflows, but understanding the underlying processing principles remains important for interpreting results correctly and recognizing potential measurement artifacts. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd supports customers not just with high-quality probe hardware but with technical expertise in measurement methodology, helping laboratories establish robust testing protocols that deliver reliable, repeatable results for their specific antenna characterization requirements.
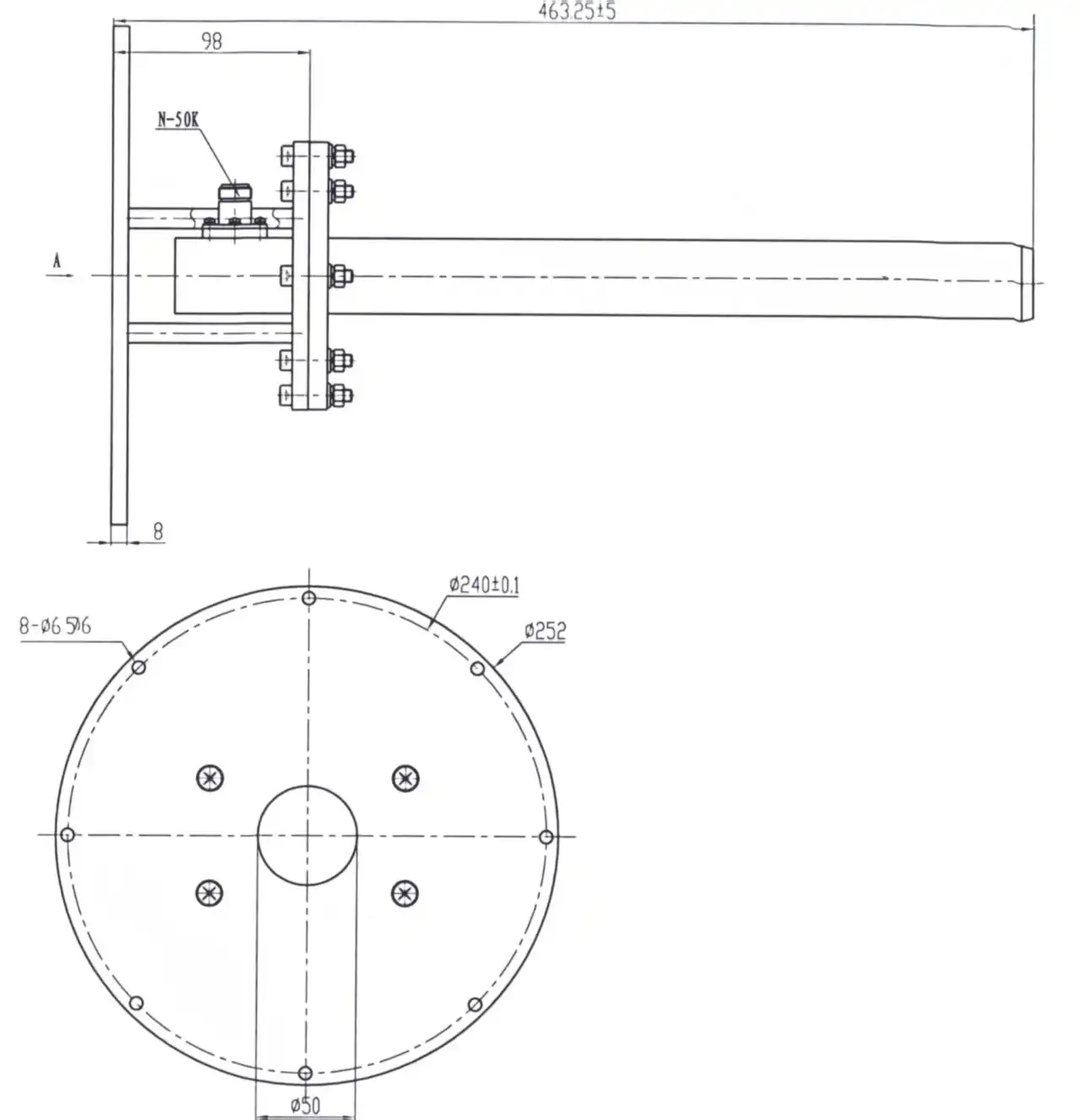
Selecting the Right Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe
Frequency Range and Probe Type Considerations
Choosing an appropriate Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe begins with carefully assessing the frequency range requirements of your measurement applications. The probe must effectively cover all operational frequencies of the antennas under test, including margins below the lowest operating frequency and above the highest frequency to ensure adequate measurement system response. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd offers probe solutions spanning from 10 MHz through 110 GHz, accommodating applications from HF communication antennas through millimeter-wave systems for 5G infrastructure and automotive radar. The wide frequency coverage ensures that laboratories can address diverse measurement needs without maintaining multiple specialized probe systems, though specific applications may benefit from optimized probe designs targeting narrower frequency bands where maximum performance is critical. The probe type selection equally influences measurement success. Electric field probes, typically implemented as open-ended waveguides or small dipole antennas, sense the electric field component of the electromagnetic wave and work well for most antenna measurement scenarios. Magnetic field probes, often realized as small loop antennas, measure the magnetic field component and prove valuable for characterizing certain antenna types or when testing in environments with specific electromagnetic interference characteristics. Dual-mode probes incorporate both electric and magnetic sensing capabilities, offering maximum measurement flexibility at the cost of increased complexity and typically higher investment. For laboratories conducting varied measurement work across different antenna types, the dual-mode Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe configuration from Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd provides comprehensive capabilities supporting planar, cylindrical, and spherical near-field measurement approaches with a single probe solution.
Calibration and Measurement Accuracy Requirements
Measurement accuracy ultimately determines whether antenna test results support critical decisions about design optimization, production quality control, or regulatory compliance. The Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe's intrinsic measurement accuracy, specified at ±0.5% for Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd's systems, represents just one component of overall measurement uncertainty. System calibration procedures must establish traceable references for probe response, positioning accuracy, and RF measurement equipment performance. Pre-calibrated probes with documented traceability streamline initial system setup and ongoing measurement quality assurance, though periodic verification and recalibration remain necessary to maintain long-term measurement confidence. Understanding the error sources affecting near-field measurements helps laboratories implement appropriate mitigation strategies. Probe positioning errors introduce phase uncertainties that become increasingly significant at higher frequencies where wavelengths shrink to millimeters. The mechanical positioning system must maintain accuracy within fractions of a wavelength, requiring careful calibration and potentially environmental controls to minimize thermal expansion effects. Multiple reflections between the probe and antenna under test can corrupt measurements, necessitating careful anechoic chamber design with adequate absorber coverage. Probe-antenna coupling effects, where the probe's presence disturbs the antenna's radiation pattern, must be minimized through proper probe design and measurement distance selection. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd's extensive experience, including their specialized 24m Microwave Darkroom facility with controlled environmental conditions and precision measurement capabilities, provides customers with expert guidance for achieving optimal measurement accuracy in their specific application contexts.
Conclusion
Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe technology has evolved from specialized research tool to essential test laboratory equipment, enabling compact, efficient, and accurate antenna characterization across industries from satellite communications to defense radar systems. The strategic advantages of reduced facility requirements, faster measurement cycles, and comprehensive performance data make near-field capabilities indispensable for organizations committed to antenna excellence.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Ready to transform your antenna testing capabilities? Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd stands as your trusted China Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe manufacturer, supplier, and factory partner with over 20 years of specialized microwave technology experience. Our High Quality Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe systems deliver proven performance across 10 MHz to 110 GHz, backed by ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, and ISO 45001:2018 certifications ensuring environmental responsibility, quality excellence, and workplace safety. Whether you need standard configurations or customized OEM solutions, our expert engineering team provides comprehensive technical support from initial consultation through installation and beyond. Our competitive Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe price and Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe for sale options combined with fast delivery through our optimized supply chain make advanced measurement technology accessible. Contact our dedicated team at craig@admicrowave.com for detailed specifications, application guidance, and pricing information. As a leading China Antenna Near Field Measurement Probe wholesale provider, we're ready to support your measurement excellence with cutting-edge technology and responsive service.
References
1. Joy, Edward B. and Paris, Demetrius T. "Spatial Sampling and Filtering in Near-Field Measurements." IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Volume AP-20, May 1972.
2. Yaghjian, Arthur D. "An Overview of Near-Field Antenna Measurements." National Bureau of Standards Technical Note, National Institute of Standards and Technology, 1986.
3. Hansen, Jørgen E. "Spherical Near-Field Antenna Measurements." IET Electromagnetic Waves Series, Institution of Engineering and Technology, 1988.
4. Newell, Allen C. and Crawford, Myron L. "Planar Near-Field Measurements on High Performance Array Antennas." National Bureau of Standards Internal Report, NBSIR 74-380, July 1974.
5. Evans, Gary E. "Antenna Measurement Techniques." Artech House Antennas and Propagation Library, Artech House Publishers, 1990.
YOU MAY LIKE
 VIEW MORELog Periodic Antenna
VIEW MORELog Periodic Antenna VIEW MORESlotted Waveguide Array Antenna
VIEW MORESlotted Waveguide Array Antenna VIEW MOREOpen Boundary Dual Linear Polarization Four Ridged Horn Antenna
VIEW MOREOpen Boundary Dual Linear Polarization Four Ridged Horn Antenna VIEW MOREConical Dual circular Polarization Horn Antenna
VIEW MOREConical Dual circular Polarization Horn Antenna VIEW MORELadder Membrane Conical Dual circular Polarization Horn Antenna
VIEW MORELadder Membrane Conical Dual circular Polarization Horn Antenna VIEW MOREDual Linear Broadband Dual Circular Polarization Horn Antenna
VIEW MOREDual Linear Broadband Dual Circular Polarization Horn Antenna VIEW MOREConical Linear Polarization Horn Antenna
VIEW MOREConical Linear Polarization Horn Antenna VIEW MOREPlanar Spiral Antenna
VIEW MOREPlanar Spiral Antenna




