What is the difference between AC and DC amplifier?
In the demanding environments of satellite communications, aerospace navigation, and defense radar systems, signal integrity can mean the difference between mission success and catastrophic failure. Engineers face a critical choice when selecting amplification technology: understanding the fundamental differences between AC and DC amplifiers. These two amplifier types employ distinct coupling methods that directly impact performance, frequency response, and application suitability. The AC Power Amplifier represents a specialized solution designed to address the unique challenges of high-frequency signal amplification, where traditional coupling methods must balance noise rejection, bandwidth requirements, and signal fidelity to ensure reliable operation across demanding frequency ranges from legacy systems to cutting-edge 5G networks.
Understanding AC and DC Amplifier Fundamentals
The terminology surrounding AC and DC amplifiers often creates confusion, as these terms do not refer to the type of current being amplified but rather to the coupling method between amplification stages. An AC amplifier, also known as a capacitor-coupled or transformer-coupled amplifier, utilizes capacitors or transformers between different stages of amplification. These coupling components serve a critical function by blocking DC voltage components while allowing AC signals to pass through unimpeded. This design approach provides inherent advantages in noise rejection and simplifies the adjustment of static operating points across multiple amplification stages. The AC Power Amplifier from Advanced Microwave Technologies exemplifies this approach, incorporating sophisticated coupling mechanisms optimized for microwave frequency applications ranging from 0.5 to 110 GHz. In contrast, DC amplifiers employ direct coupling between amplification stages without the use of capacitors or transformers in the signal path. This direct-coupled configuration creates a cleaner circuit topology but introduces different design challenges. DC amplifiers can amplify signals from zero frequency upward, making them essential for applications requiring true DC response or extremely low-frequency signal amplification. However, this capability comes with the trade-off of increased complexity in managing static operating points and greater susceptibility to zero drift, where small variations in component characteristics can cause significant output offset even with no input signal applied.
Coupling Methods and Circuit Topology
The coupling method fundamentally shapes amplifier performance characteristics and application suitability. In AC-coupled amplifiers, capacitors act as high-pass filters that eliminate DC offset voltages while preserving the AC signal components. This blocking action ensures that each amplification stage operates independently with its own optimized biasing conditions. For high-frequency applications such as satellite communications and radar systems, this independence simplifies circuit design and enhances reliability. The Ac Power Amplifier utilizes advanced coupling techniques specifically engineered for microwave frequencies, where conventional capacitors must be carefully selected to minimize parasitic effects that could degrade signal quality at frequencies extending into the millimeter-wave spectrum. Transformer coupling offers additional benefits in AC amplifier designs, particularly for impedance matching between stages with different input and output impedances. Transformers provide galvanic isolation between stages while simultaneously allowing voltage and current transformation through carefully calculated winding ratios. This capability proves invaluable in RF and microwave applications where matching network design directly impacts power transfer efficiency. Advanced Microwave Technologies incorporates these principles in their AC Power Amplifier designs, optimizing impedance matching across broad frequency ranges to maximize power delivery to loads such as antenna feed networks and waveguide assemblies.
Frequency Response and Bandwidth Considerations
Frequency response characteristics represent one of the most significant distinctions between AC and DC amplifiers, directly impacting their suitability for specific applications. AC amplifiers exhibit a high-pass frequency response determined by the coupling capacitor values and circuit impedances. The lower cutoff frequency occurs where the capacitive reactance equals the circuit impedance, below which signal attenuation increases. For audio and RF applications, this high-pass behavior advantageously eliminates low-frequency noise and interference while passing the desired signal band. The Ac Power Amplifier from Advanced Microwave Technologies demonstrates exceptional bandwidth performance, maintaining flat frequency response across the 0.5 to 110 GHz range essential for modern satellite communications, 5G infrastructure, and advanced radar systems. DC amplifiers provide frequency response extending from zero Hz upward, enabling amplification of extremely slow-varying signals and true DC voltages. This capability makes DC amplifiers indispensable for instrumentation, sensor signal conditioning, and applications requiring preservation of signal baseline information. However, the extended low-frequency response also means DC amplifiers remain susceptible to drift, low-frequency noise, and thermal effects that AC coupling would naturally reject. In high-performance microwave applications, the choice between AC and DC coupling depends on signal characteristics, required bandwidth, and environmental operating conditions.
Signal Integrity and Noise Performance
Signal integrity considerations drive amplifier selection in critical communications and defense applications. AC-coupled amplifiers inherently reject DC offset voltages and low-frequency interference, providing cleaner signal amplification in electrically noisy environments. This noise rejection capability proves particularly valuable in aerospace and defense applications where electromagnetic interference from adjacent systems could compromise signal quality. The forced air cooling system integrated into Advanced Microwave's Ac Power Amplifier maintains optimal operating temperatures, further minimizing thermal noise that could degrade signal-to-noise ratios in sensitive receiver applications. The phase shift introduced by coupling capacitors in AC amplifiers must be carefully managed across the operating frequency range. Each capacitive coupling network introduces a frequency-dependent phase shift that accumulates across multiple amplification stages. For applications requiring precise phase linearity, such as phased array radar systems and precision navigation equipment, amplifier designers must optimize coupling networks to maintain phase coherence across the operational bandwidth. Advanced Microwave Technologies addresses these requirements through rigorous testing in their 24-meter Microwave Darkroom, where far-field antenna patterns and amplifier phase linearity can be characterized with exceptional precision.
Application-Specific Amplifier Selection
The choice between AC and DC amplification technology directly impacts system performance in telecommunications infrastructure. In satellite ground stations handling HD video, data, and voice communications, the Ac Power Amplifier provides the high-power, broadband amplification necessary for efficient uplink signal transmission. The wide frequency support inherent in AC-coupled designs accommodates multiple communication bands simultaneously, from legacy C-band and Ku-band systems to emerging Ka-band and millimeter-wave links. This versatility enables ground station operators to support diverse satellite constellations with a single amplifier platform, reducing equipment costs and simplifying maintenance procedures. Military surveillance radar systems demand amplifiers capable of generating high-power pulses with fast rise times and minimal distortion. The AC Power Amplifier's stable signal transmission characteristics ensure that radar waveforms maintain their designed spectral properties throughout the amplification process. This spectral purity directly translates to improved target detection range and enhanced ability to distinguish between closely spaced objects. The compact 19-inch rackmount design facilitates integration into mobile radar platforms, shipboard systems, and airborne surveillance equipment where space constraints and weight limitations impose strict requirements on component selection.
Weather Monitoring and Direction Finding Applications
Weather radar systems operating in X-band frequencies rely on precise amplification of transmitted pulses and sensitive reception of reflected signals from precipitation and atmospheric phenomena. The Ac Power Amplifier's low noise characteristics minimize false targets caused by amplifier-generated noise, improving weather radar sensitivity and detection capability. For Doppler weather radar systems measuring wind velocities and precipitation intensity, the amplifier's stable gain and phase response across temperature variations ensures accurate velocity measurements even during extreme weather events. The ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturing processes employed by Advanced Microwave Technologies guarantee consistent amplifier performance across production units, critical for meteorological networks requiring uniform calibration across multiple radar installations. Direction finding systems used for navigation and signal intelligence applications require amplifiers maintaining consistent gain and phase characteristics across their operating frequency range. The Ac Power Amplifier's careful phase linearity enables precise determination of signal arrival angles, essential for navigation aids and electronic warfare systems. UAV communication links benefit from the amplifier's high efficiency, which translates directly to reduced prime power requirements and extended mission endurance. For security checkpoint systems utilizing millimeter-wave imaging technology, the amplifier's extended frequency coverage to 110 GHz enables high-resolution imaging for concealed threat detection.
Advanced Design Features and Customization
Advanced Microwave Technologies' commitment to customization enables system integrators to optimize the Ac Power Amplifier for specific mission requirements. OEM services provide tailored frequency ranges matching exact application needs, whether narrowband optimization for single-frequency radar systems or broadband coverage for multi-mission platforms. Custom output power specifications allow designers to match amplifier capability precisely to load requirements, avoiding over-specification that increases cost and under-specification that compromises performance margins. This flexibility proves particularly valuable in aerospace and defense programs where unique operational requirements demand specialized solutions not available in commercial off-the-shelf products. The advanced cooling mechanism incorporated into the Ac Power Amplifier design maintains junction temperatures within safe operating limits even during prolonged high-power operation. Forced air cooling provides superior thermal management compared to passive heat sinking alone, enabling higher power density packaging while ensuring reliability across the military temperature range. For applications in challenging thermal environments, such as desert deployments or tropical maritime operations, effective thermal management directly determines system availability and mission readiness. The amplifier's thermal design has been validated through extensive environmental testing, confirming performance across temperature extremes from Arctic cold to desert heat.
Integration with Modern Communication Systems
Modern 5G and emerging 6G wireless infrastructure demands amplifiers capable of handling complex modulation formats and wide channel bandwidths. The Ac Power Amplifier's linear transfer characteristics minimize intermodulation distortion that could create interference in adjacent frequency channels. This linearity becomes increasingly critical as spectrum regulations tighten and wireless carriers deploy advanced modulation schemes to maximize spectral efficiency. The amplifier's wide frequency support accommodates the diverse frequency bands allocated for 5G deployment globally, from sub-6 GHz bands to millimeter-wave frequencies above 24 GHz. For rural broadband deployment using fixed wireless access technology, the amplifier's high output power extends coverage to underserved areas where fiber infrastructure proves economically impractical. Industrial IoT applications increasingly rely on wireless connectivity for sensor networks, asset tracking, and predictive maintenance systems. The Ac Power Amplifier enables long-range connectivity for these applications, reducing infrastructure costs by minimizing the number of base stations required for coverage. In smart agriculture implementations, amplified sensor networks monitor soil conditions, weather parameters, and crop health across large farm operations, enabling precision agriculture techniques that optimize resource utilization. For smart cities infrastructure, amplified communication links connect traffic management systems, environmental monitoring stations, and public safety networks into cohesive urban management platforms.
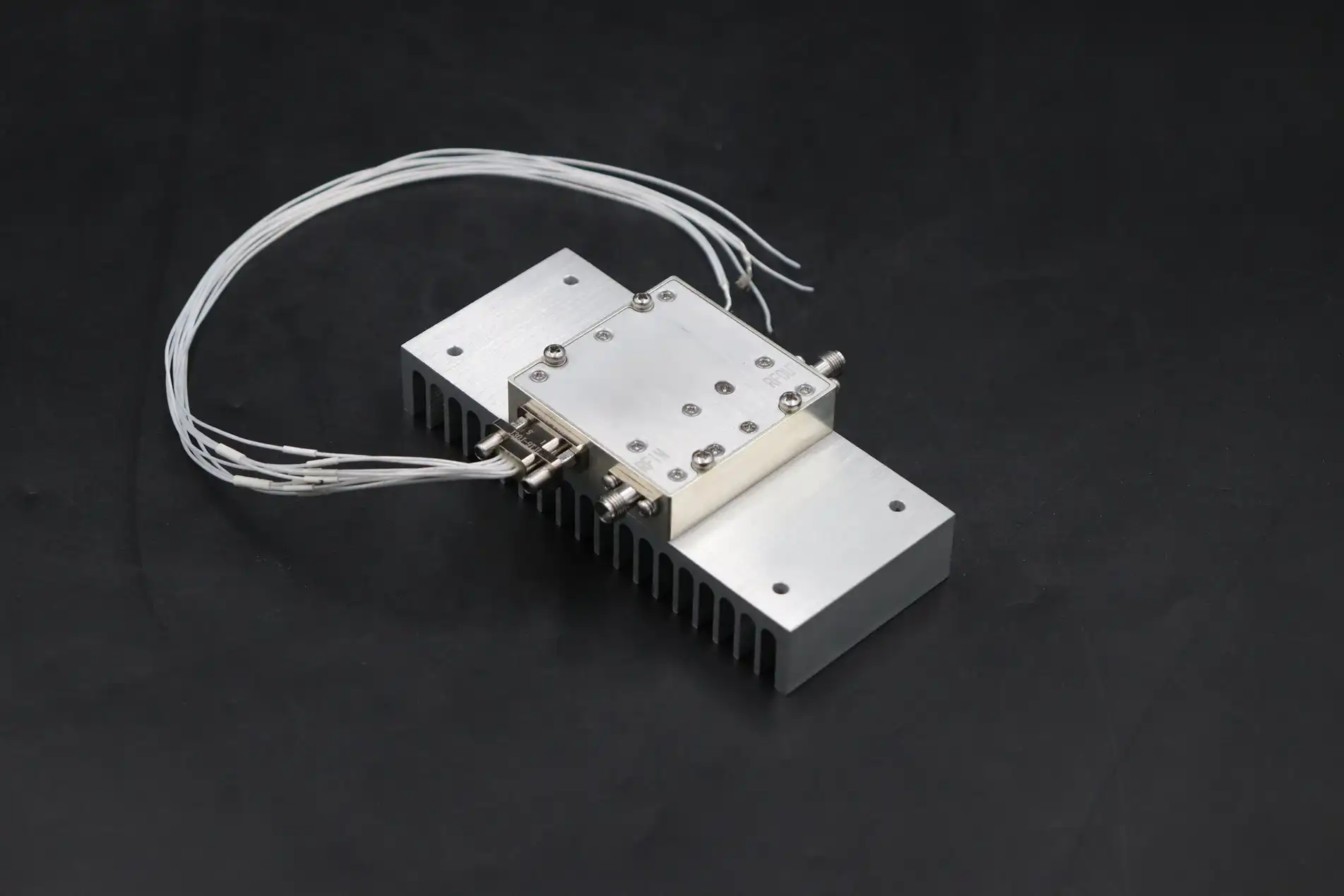

Quality Assurance and Manufacturing Excellence
Advanced Microwave Technologies' ISO 9001:2015 certification demonstrates systematic quality management throughout the Ac Power Amplifier manufacturing process. From initial component selection through final testing, documented procedures ensure consistent product quality and performance. The company's 24-meter Microwave Darkroom provides unparalleled measurement capability for characterizing amplifier performance across the full operating frequency range. Far-field antenna measurements verify amplifier compatibility with various antenna configurations, while near-field measurements identify potential issues with radiation pattern distortion or unwanted coupling effects. This comprehensive testing capability, spanning frequencies from 0.5 to 110 GHz, ensures that every Ac Power Amplifier meets published specifications before shipment. Environmental stewardship embodied in the company's ISO 14001:2015 certification extends to responsible manufacturing practices minimizing waste generation and energy consumption. Advanced Microwave's commitment to reducing environmental impact aligns with global sustainability initiatives while ensuring product quality remains uncompromised. The ISO 45001:2018 occupational health and safety standard implementation protects employees working with sophisticated microwave test equipment and manufacturing processes, creating a workplace culture emphasizing safety and continuous improvement. These certifications collectively demonstrate organizational excellence extending beyond technical capability to encompass social responsibility and employee welfare.
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamental differences between AC and DC amplifiers enables informed selection of amplification technology optimized for specific applications. The Ac Power Amplifier represents advanced engineering addressing the unique challenges of high-frequency signal amplification in demanding telecommunications, aerospace, and defense environments where performance, reliability, and signal integrity determine mission success.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd stands as a trusted China Ac Power Amplifier manufacturer with over 20 years of microwave expertise. As a leading China Ac Power Amplifier supplier and China Ac Power Amplifier factory, we provide High Quality Ac Power Amplifier solutions with competitive Ac Power Amplifier price points. Our Ac Power Amplifier for sale includes customizable options and China Ac Power Amplifier wholesale programs. Contact craig@admicrowave.com for inquiries on waveguides, coaxial assemblies, microwave antennas, and satellite communication components. Bookmark this resource for future reference.
References
1. Bennett, William R. "Introduction to Signal Transmission: Transmission, Noise, and Distortion." McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1970.
2. Krauss, Herbert L., Charles W. Bostian, and Frederick H. Raab. "Solid State Radio Engineering." John Wiley & Sons, 1980.
3. Pozar, David M. "Microwave Engineering." John Wiley & Sons, Fourth Edition, 2011.
4. Sechi, Franco and Marina Bujatti. "Solid-State Microwave High-Power Amplifiers." Artech House Publishers, 2009.












