How to Choose the Best Planar Spiral Antenna for Multi-Band Use?
When designing modern communication systems that demand operation across multiple frequency bands simultaneously, engineers face a critical challenge: selecting an antenna that delivers consistent performance without requiring multiple hardware configurations. The Planar Spiral Antenna emerges as the definitive solution for multi-band applications, offering exceptional bandwidth coverage from 1 GHz to 40 GHz while maintaining stable impedance characteristics and circular polarization throughout its operational range. This comprehensive guide examines the essential criteria for selecting the optimal Planar Spiral Antenna configuration, addressing the technical specifications, performance parameters, and practical considerations that determine success in satellite communications, aerospace defense systems, electronic reconnaissance, and advanced telecommunications infrastructure.
Understanding Planar Spiral Antenna Multi-Band Capabilities
The fundamental advantage of the Planar Spiral Antenna for multi-band applications stems from its inherent frequency-independent design characteristics. Unlike conventional antenna systems that require separate elements for different frequency bands, the spiral geometry creates a self-complementary structure where impedance, radiation pattern, and polarization remain remarkably consistent across an extraordinarily wide bandwidth. This frequency independence results from the antenna's progressive radiation mechanism, where different regions of the spiral structure resonate at different frequencies—lower frequencies radiate from the outer spiral regions where the circumference approaches one wavelength, while higher frequencies activate the inner spiral regions. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd has refined this design principle to achieve bandwidth ratios exceeding forty-to-one, enabling a single Planar Spiral Antenna to replace what would traditionally require five or more narrowband antenna elements in multi-band communication systems.
The ultra-wideband performance extends beyond simple frequency coverage to encompass consistent electrical characteristics throughout the operational spectrum. The Planar Spiral Antenna maintains low VSWR values typically below two-to-one across its entire frequency range, ensuring minimal signal reflection and maximum power transfer efficiency regardless of the operating frequency. This stability proves invaluable in software-defined radio applications and cognitive radio systems where frequency agility is essential, allowing seamless transitions between frequency bands without performance degradation or the need for complex matching networks. The circular polarization inherent to the spiral configuration provides additional multi-band advantages, as the polarization characteristic remains consistent across all operational frequencies, simplifying system design and enhancing signal reliability in multipath environments. For organizations implementing multi-band radar systems, satellite communication ground stations, or electronic warfare platforms, this comprehensive frequency coverage with stable performance characteristics represents a fundamental architectural advantage that significantly reduces system complexity while improving overall reliability.
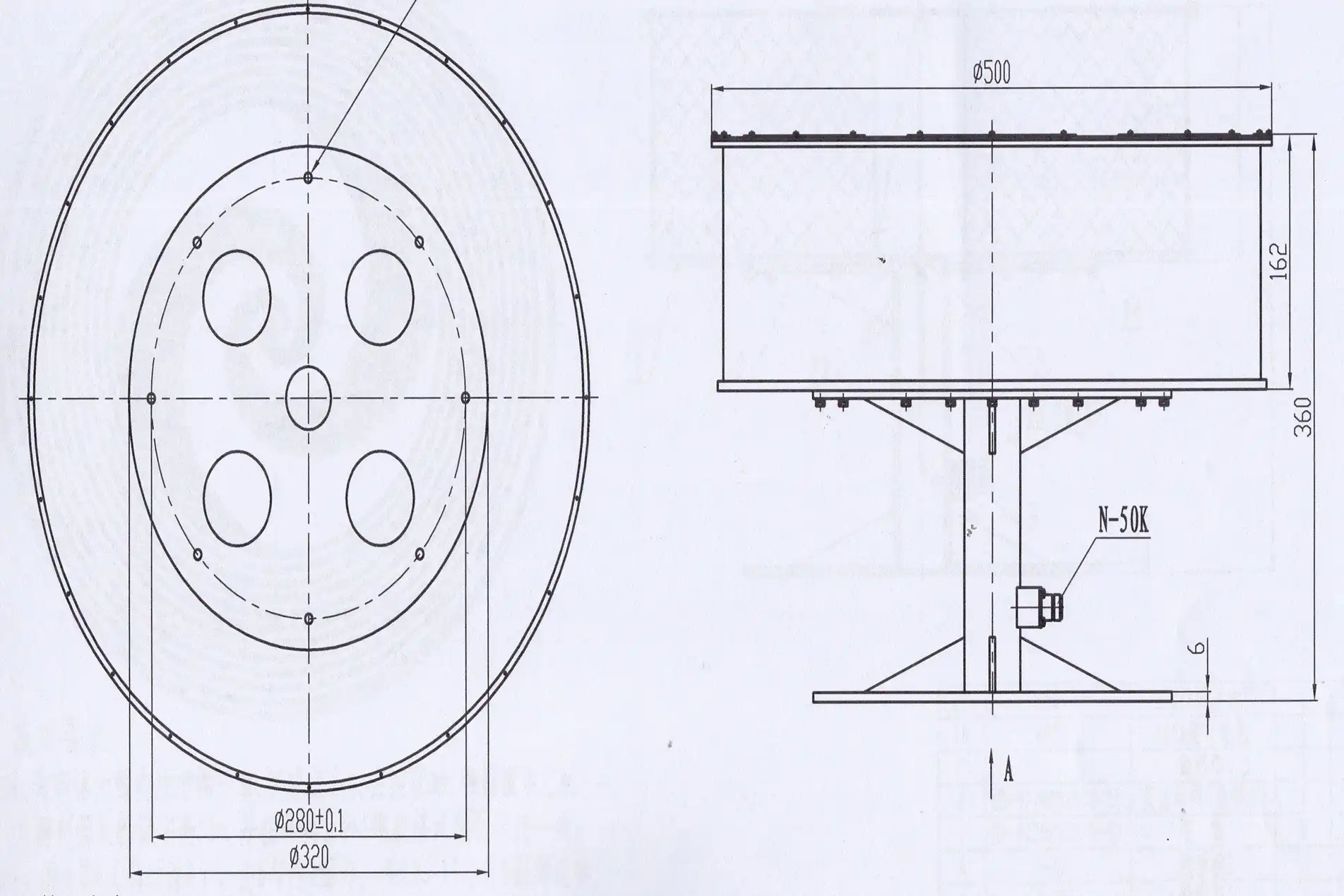
Critical Frequency Range Specifications for Multi-Band Operation
Selecting the appropriate frequency range represents the most critical decision when specifying a Planar Spiral Antenna for multi-band applications. The operational bandwidth must encompass all required frequency bands with sufficient margin to account for environmental variations, aging effects, and future expansion requirements. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd manufactures Planar Spiral Antennas with frequency ranges spanning from one gigahertz up to forty gigahertz, providing comprehensive coverage for most modern communication and radar applications including L-band satellite communications, S-band weather radar, C-band fixed satellite services, X-band military communications, Ku-band direct broadcast satellite, and portions of the Ka-band for high-throughput satellite systems. The lower frequency limit is determined primarily by the outer diameter of the spiral structure, as the antenna becomes electrically small and inefficient when its overall size drops below approximately one-third wavelength. Engineers must carefully evaluate whether the required lowest operational frequency can be accommodated within acceptable physical dimensions, or whether alternative antenna configurations should be considered.
The upper frequency limit is constrained by the initial spiral radius at the feed point, manufacturing precision limitations, and the performance characteristics of the balun structure that transforms the balanced spiral impedance to an unbalanced coaxial feed. For multi-band applications requiring operation into millimeter-wave frequencies above thirty gigahertz, particular attention must be paid to conductor surface finish, dielectric material selection, and mechanical stability, as these factors increasingly impact performance at shorter wavelengths. Advanced Microwave's Planar Spiral Antenna designs incorporate precision manufacturing techniques and advanced materials to maintain performance consistency up to forty gigahertz, but applications requiring even higher frequency operation may necessitate custom engineering to address the specific challenges associated with millimeter-wave propagation. When defining frequency range requirements, engineers should also consider the antenna's gain variation across the operational bandwidth—while the Planar Spiral Antenna provides relatively flat gain response throughout most of its range, gain typically decreases at the lowest frequencies where the antenna becomes electrically small, potentially impacting link budget calculations for multi-band systems that must maintain consistent performance across all operational frequencies.
Impedance Matching and VSWR Considerations Across Multiple Bands
Impedance matching represents a critical performance parameter for multi-band Planar Spiral Antenna applications, as poor impedance matching results in reflected power that reduces transmit efficiency, degrades receiver sensitivity, and can potentially damage power amplifier stages in transmit applications. The Planar Spiral Antenna exhibits inherently broadband impedance characteristics, typically maintaining a fifty-ohm input impedance with variations of plus or minus ten ohms across its operational bandwidth. This stable impedance behavior contrasts sharply with resonant antenna designs where impedance varies dramatically with frequency, requiring complex matching networks that introduce loss and constrain operational bandwidth. The voltage standing wave ratio directly quantifies impedance matching quality, representing the ratio between maximum and minimum voltage amplitudes along a transmission line. Advanced Microwave's Planar Spiral Antennas routinely achieve VSWR values below two-to-one across their entire specified frequency range, corresponding to return loss values exceeding ten decibels and reflected power percentages below eleven percent. For demanding multi-band applications where maximum efficiency is paramount, VSWR specifications below one-point-five-to-one may be achievable through careful design optimization and precision manufacturing.
The balun structure that transforms the balanced impedance of the spiral radiating element to the unbalanced impedance of the coaxial feed system plays a crucial role in achieving low VSWR performance across multiple frequency bands. Various balun configurations exist, including Marchand baluns, tapered microstrip transitions, and exponential taper designs, each offering different trade-offs between bandwidth, physical size, and impedance transformation ratio. Advanced Microwave Technologies employs sophisticated balun designs optimized for ultra-wideband operation, ensuring that the balun performance does not become the limiting factor in overall antenna bandwidth. When evaluating Planar Spiral Antenna options for multi-band systems, engineers should request measured VSWR data across the entire operational frequency range rather than relying solely on specification limits at discrete test frequencies. This comprehensive VSWR characterization reveals any resonances, impedance discontinuities, or bandwidth limitations that might impact performance in specific frequency bands. For applications involving high transmit power levels, VSWR specifications become even more critical, as reflected power not only reduces radiated power but can also create voltage standing waves that exceed the power handling capability of transmission line components or the antenna structure itself. Planar Spiral Antennas designed for electronic reconnaissance or receive-only applications can often tolerate slightly higher VSWR values, but transmit applications demand stringent impedance matching to protect power amplifiers and maximize radiated power efficiency across all operational frequency bands.
Polarization Purity Requirements for Multi-Band Systems
The circular polarization characteristic of the Planar Spiral Antenna provides significant advantages for multi-band applications, particularly in satellite communications, radar systems, and mobile platforms where antenna orientation relative to the signal source may vary during operation. Unlike linearly polarized antennas that suffer severe signal degradation when misaligned with the incoming signal polarization, circularly polarized antennas maintain consistent performance regardless of rotational orientation around the antenna's boresight axis. This polarization independence proves invaluable in mobile satellite terminals, aircraft communications, and maritime systems where maintaining precise antenna alignment is impractical or impossible. The direction of circular polarization—either right-hand or left-hand—is determined by the spiral's rotational direction, with clockwise spirals producing right-hand circular polarization and counterclockwise spirals generating left-hand circular polarization. Most satellite communication systems utilize right-hand circular polarization for downlink transmissions and left-hand circular polarization for uplink transmissions, allowing frequency reuse and isolation between transmit and receive channels.
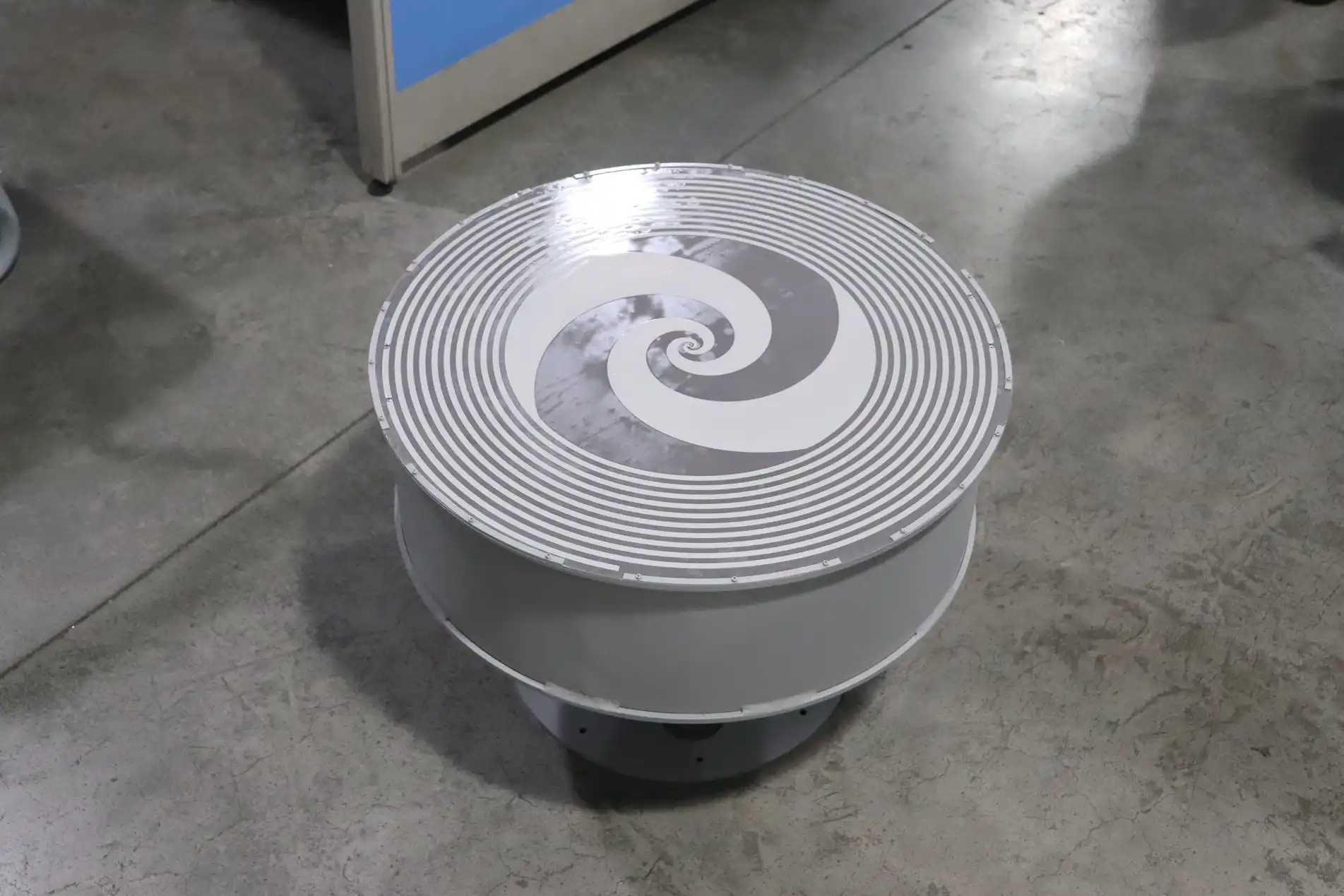

Advanced Microwave's Planar Spiral Antennas maintain excellent polarization purity across their entire operational bandwidth, typically achieving axial ratio values below three decibels on boresight and below six decibels across the antenna's primary coverage area. The axial ratio quantifies the ellipticity of the polarization, with lower values indicating purer circular polarization and improved performance in multipath environments. For multi-band systems operating in challenging propagation conditions where signals may be reflected from buildings, terrain features, or atmospheric layers, the circular polarization of the Planar Spiral Antenna provides inherent multipath rejection, as single-reflection multipath signals undergo polarization reversal and are significantly attenuated by the receiving antenna's polarization discrimination. This characteristic proves particularly valuable in urban communication systems, ground-based radar installations, and electronic warfare applications where multipath interference would otherwise degrade system performance. When specifying polarization requirements for multi-band Planar Spiral Antenna systems, engineers should consider not only the axial ratio on boresight but also the polarization stability across the antenna's coverage pattern and throughout the operational frequency range. Advanced Microwave Technologies provides comprehensive polarization characterization data including axial ratio as a function of elevation and azimuth angles across multiple frequency bands, enabling system designers to accurately predict polarization performance in their specific application environment.
Physical Integration and Mounting Considerations
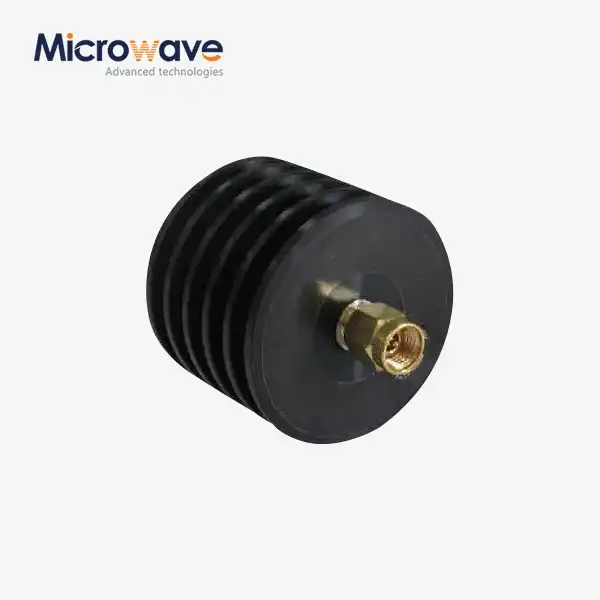
The compact, low-profile form factor of the Planar Spiral Antenna represents a significant practical advantage for multi-band systems with space constraints or weight limitations. The planar spiral design achieves its wideband performance within a cylindrical envelope typically measuring one-third wavelength in diameter at the lowest operational frequency and one-quarter wavelength in depth, dimensions that compare favorably with alternative wideband antenna technologies such as log-periodic arrays or multiple narrowband elements. This compact size simplifies integration into airborne platforms, small satellite ground terminals, portable electronic reconnaissance systems, and array configurations where multiple antenna elements must be accommodated within limited aperture areas. The lightweight construction utilizing precision-machined metal spiral elements bonded to low-loss dielectric substrates results in antenna assemblies weighing significantly less than equivalent horn antennas or reflector systems, reducing structural loading on mounting platforms and simplifying pointing mechanisms for mobile installations. Advanced Microwave Technologies offers customizable Planar Spiral Antenna configurations with mounting options including standard threaded flanges, quick-disconnect interfaces, and integrated mounting brackets designed to accommodate various platform requirements while maintaining mechanical stability and electrical performance.
The absorber-loaded cavity that backs the spiral radiating element serves multiple critical functions including suppression of back radiation, improvement of radiation pattern symmetry, and absorption of surface waves that would otherwise degrade antenna performance. However, the cavity and absorber materials introduce constraints on power handling capability and thermal management requirements that must be considered during system integration. The absorbing material, typically a magnetically loaded dielectric composite, dissipates received and internally reflected power as heat, creating thermal gradients that can affect antenna performance in high-power applications or extreme environmental conditions. For multi-band systems with significant transmit power requirements, Advanced Microwave provides enhanced thermal management options including conductive backing plates, finned heat sink structures, and forced-air cooling provisions to maintain acceptable operating temperatures. The environmental sealing of the antenna assembly represents another critical integration consideration, as the spiral elements, balun structure, and cavity absorber must be protected from moisture ingress, temperature extremes, ultraviolet radiation exposure, and mechanical shock and vibration. Advanced Microwave's Planar Spiral Antennas incorporate comprehensive environmental protection including weatherproof radomes, sealed connector interfaces, and ruggedized construction suitable for demanding aerospace, maritime, and outdoor terrestrial applications where reliability across multiple frequency bands must be maintained regardless of environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal Planar Spiral Antenna for multi-band applications requires careful evaluation of frequency range, impedance characteristics, polarization performance, and physical integration constraints to ensure reliable operation across all required frequency bands while meeting system size, weight, and environmental requirements.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd stands as your premier China Planar Spiral Antenna factory, delivering over twenty years of microwave engineering excellence through our state-of-the-art 24m Microwave Darkroom facility equipped with measurement capabilities spanning 0.5 to 110 GHz. As a trusted China Planar Spiral Antenna supplier and leading China Planar Spiral Antenna manufacturer, we provide comprehensive OEM services including custom frequency ranges, materials optimization, and rapid prototyping with global supply chain management ensuring timely delivery. Our High Quality Planar Spiral Antenna solutions combine ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, and ISO 45001:2018 certifications with competitive Planar Spiral Antenna price structures, making us your ideal China Planar Spiral Antenna wholesale partner. Our Planar Spiral Antenna for sale offerings feature customizable designs from 1 GHz to 40 GHz with professional technical support from our expert engineering team. Contact our team at craig@admicrowave.com to discuss your multi-band antenna requirements and discover how our advanced testing capabilities, strict quality control, and strong after-sales support can optimize your communication systems. Bookmark this guide for future reference when specifying antenna solutions for your next project.
References
1. Curtis, J. A. (1960). Spiral Antennas. IRE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Institute of Radio Engineers.
2. Dyson, J. D. (1959). The Equiangular Spiral Antenna. IRE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
3. Nakano, H., Mimaki, H., and Yamauchi, J. (1988). Backfire Radiation from a Monofilar Spiral Antenna with a Cavity-Backed Small Reflector. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
4. Kaiser, J. A. (1960). The Archimedean Two-Wire Spiral Antenna. IRE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Institute of Radio Engineers.
5. Corzine, R. G. and Mosko, J. A. (1990). Four-Arm Spiral Antennas. Artech House Antenna Library, Artech House Publishers.





_1733809032116.webp)



_1733738410152.webp)


