Best Waveguide Flange Gasket Materials for Low Insertion Loss
When signal degradation threatens your critical microwave system performance, every connection point becomes a potential failure zone. The best waveguide flange gasket materials for achieving low insertion loss combine high electrical conductivity with superior mechanical sealing properties, specifically conductive elastomers such as silver-filled silicone and silver-plated copper-filled materials. These advanced Waveguide Flange Gasket solutions ensure minimal signal attenuation while maintaining electromagnetic integrity across frequencies reaching 110 GHz. Engineers facing challenges with RF leakage, environmental contamination, or inconsistent system performance will discover how material selection directly impacts transmission efficiency, system reliability, and long-term operational costs in demanding aerospace, telecommunications, and defense applications.
Understanding Material Properties Critical for Low Insertion Loss in Waveguide Flange Gaskets
The foundation of superior waveguide system performance rests upon selecting gasket materials that deliver both exceptional electrical conductivity and reliable mechanical compression characteristics. In microwave transmission systems operating across frequencies from 500 MHz to 110 GHz, the Waveguide Flange Gasket serves as more than a simple sealing component—it functions as a critical electrical interface that must maintain continuous current flow across the flange junction. When electromagnetic energy propagates through a waveguide, surface currents travel along the inner walls, and any discontinuity at the flange connection creates impedance mismatches that manifest as insertion loss and signal reflections. Conductive elastomer materials have emerged as the industry standard for achieving minimal insertion loss because they combine the electrical properties of metals with the conformability of rubber compounds. Silver-filled silicone elastomers, particularly formulations incorporating high concentrations of silver particles uniformly dispersed throughout the polymer matrix, provide volume resistivity values below 0.005 ohm-cm, ensuring that the gasket presents negligible electrical resistance compared to the waveguide walls themselves. This low resistivity translates directly to reduced insertion loss, with properly installed Waveguide Flange Gasket systems exhibiting typical insertion losses below 0.05 dB across operational frequency ranges.
The mechanical properties of gasket materials prove equally important for long-term performance stability. Materials must exhibit sufficient compressibility to conform to minor surface imperfections on machined flanges while maintaining enough structural integrity to prevent cold flow under sustained compression. Advanced formulations incorporate expanded metal reinforcements within the elastomer matrix, which eliminates creep and relaxation over time while preserving the material's ability to maintain consistent electrical contact pressure across the entire flange interface. Temperature stability represents another critical material parameter, as waveguide systems frequently operate in environments ranging from -55°C in aerospace applications to +125°C in high-power transmission scenarios.
Silver-Filled Silicone Elastomers for Optimal Conductivity
Silver-filled silicone elastomers represent the premier material choice for Waveguide Flange Gasket applications demanding the absolute lowest insertion loss combined with outstanding environmental durability. These specialized compounds typically contain 70-85% silver by weight, achieving this high loading through precise particle size distribution and advanced processing techniques that ensure uniform metal dispersion without compromising the elastomer's flexibility. The silver particles create numerous conductive pathways through the material thickness, effectively transforming an inherently insulating polymer into a highly conductive composite that maintains electrical continuity even under dynamic vibration and thermal cycling conditions. The manufacturing process for silver-filled silicone gaskets involves molding operations that produce O-ring and D-ring cross-sections specifically engineered for grooved flange configurations. These molded profiles provide controlled compression characteristics, with the cross-sectional geometry designed to deliver optimal contact pressure distribution across the sealing surface. When compressed between choke flanges or gasket-type flanges, the silver-filled silicone deforms to fill surface irregularities while the silver particles establish multiple electrical contact points, creating parallel conductive paths that minimize junction resistance. This multi-point contact architecture proves particularly valuable for high-frequency applications where skin effect concentrates currents near conductor surfaces, as the numerous silver contact points ensure low-resistance pathways regardless of current distribution patterns. Environmental resistance capabilities of silver-filled silicone formulations enable reliable operation across diverse installation environments. The silicone polymer matrix inherently resists oxidation, ozone attack, and UV degradation, maintaining its mechanical properties through decades of outdoor exposure in satellite communication ground stations and radar installations. The silver filler provides natural antimicrobial properties that prevent biological contamination in humid tropical environments, while the material's hydrophobic characteristics repel moisture that could otherwise compromise electrical performance or promote corrosion at the waveguide-gasket interface.
Silver-Plated Copper-Filled Materials for Enhanced Performance
Silver-plated copper-filled silicone formulations deliver an alternative Waveguide Flange Gasket material option that balances exceptional electrical performance with optimized mechanical properties for flat flange and cover flange configurations. These die-cut gaskets utilize sheet stock materials where copper particles serve as the primary conductive filler, with silver plating on each particle surface providing superior oxidation resistance and reduced contact resistance compared to bare copper. The dual-metal architecture combines copper's excellent bulk conductivity with silver's superior surface properties, resulting in materials exhibiting volume resistivity values comparable to pure silver-filled compounds while offering enhanced dimensional stability for precision flat gasket applications. The sheet stock manufacturing process enables production of gaskets with precisely controlled thickness tolerances, typically 0.027 inches with deviation limited to ±0.005 inches, ensuring consistent compression characteristics across production lots. This dimensional consistency proves critical for systems requiring specific compression set values to achieve optimal electrical contact without over-stressing flange bolts or distorting waveguide apertures. Expanded metal reinforcement layers embedded within the silver-plated copper-filled sheets prevent material flow under compression, maintaining gasket thickness and contact pressure throughout the operational lifetime even in high-vibration aerospace and shipboard installations.
Die-cutting operations produce flat Waveguide Flange Gasket configurations with apertures precisely matched to waveguide internal dimensions, with some designs incorporating slightly raised lips around the iris opening for high-pressure and high-power applications. These raised features concentrate contact pressure at the most critical sealing zone immediately surrounding the waveguide aperture, where electromagnetic field intensity reaches maximum levels and any gap or discontinuity would cause severe signal degradation. The combination of precision die-cutting and controlled material properties enables these gaskets to maintain insertion loss values below 0.03 dB while simultaneously providing environmental sealing sufficient for waveguide pressurization up to several PSI.
Comparing D-Type and O-Type Waveguide Flange Gasket Configurations
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd. offers Waveguide Flange Gasket solutions in both D-type and O-type cross-sectional configurations, each optimized for specific flange geometries and installation requirements. The fundamental distinction between these profiles relates to how the gasket deforms under compression and how that deformation pattern affects both electrical contact and environmental sealing performance. Understanding the mechanical behavior and electrical characteristics of each configuration enables engineers to select the optimal gasket type for their specific waveguide system architecture, frequency range, and environmental exposure conditions. O-type gaskets feature circular cross-sections that provide omnidirectional compression characteristics, deforming uniformly in all radial directions when compressed between flange surfaces. This symmetric deformation pattern proves particularly advantageous for grooved flange configurations where the gasket must seal against both horizontal and vertical surfaces simultaneously. The circular profile creates consistent contact pressure around its entire perimeter, establishing both the electrical continuity required for low insertion loss and the mechanical seal necessary for environmental protection. O-ring Waveguide Flange Gasket designs typically install into circular grooves machined into choke flanges or gasket-type flanges, where the groove geometry controls compression percentage and prevents gasket extrusion under operational pressures.
D-type gasket configurations utilize a cross-section combining a flat base with a rounded top surface, creating an asymmetric profile that concentrates contact pressure along the flat base while the rounded top accommodates minor flange surface variations. This geometry proves optimal for applications where one flange surface remains flat while the opposing surface contains a groove, as the flat gasket base establishes broad electrical contact with the planar surface while the rounded top seals effectively against the groove sidewalls. The increased contact area provided by the D-profile's flat base reduces contact resistance compared to equivalent-size O-rings, potentially lowering insertion loss by 10-15% in systems operating above 40 GHz where surface resistance effects become increasingly significant.
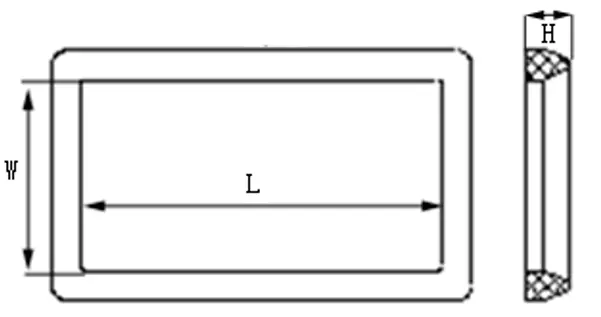
Installation Considerations for Maximum Performance
Proper installation procedures prove absolutely critical for achieving the low insertion loss performance potential inherent in high-quality Waveguide Flange Gasket materials. Even premium silver-filled silicone or silver-plated copper formulations will exhibit degraded performance if installation practices introduce contamination, create uneven compression, or allow gasket misalignment. Establishing rigorous installation protocols and training technicians in proper procedures ensures that material performance capabilities translate into actual system performance across production installations. Flange surface preparation begins with thorough cleaning to remove any dust, metal particles, oxidation, or residual lubricants from previous connections. Microscopic contamination particles create gaps in the flange-gasket interface that interrupt electrical current flow, increasing contact resistance and insertion loss. Cleaning solvents should be selected to effectively dissolve oils and greases without leaving residues, with isopropyl alcohol providing effective cleaning for most applications. Following solvent cleaning, compressed air removes any remaining particles, with final inspection under magnification recommended for critical high-power or ultra-low-loss installations.
Gasket placement and flange alignment require careful attention to prevent gasket damage or misalignment that could compromise performance. The Waveguide Flange Gasket should be removed from protective packaging immediately before installation to minimize exposure to airborne contaminants, and some applications benefit from applying a thin coating of silicone grease lubricant such as Dow Corning DC-4 to facilitate gasket positioning and initial compression. Flange bolts should be inserted and hand-tightened in a star pattern to ensure parallel compression across the entire flange interface, followed by torque wrench tightening to manufacturer specifications. Proper bolt torque proves essential, as insufficient tightening leaves gaps that increase insertion loss while excessive torque can damage gaskets or distort waveguide apertures. The recommended force for waveguide flange connections typically reaches 1000 pounds per linear inch of flange perimeter for high-power applications, translating this specification into specific bolt torque values based on flange size, bolt pattern, and bolt diameter. This substantial compression force ensures that the Waveguide Flange Gasket materials deform sufficiently to fill surface irregularities and establish the multiple electrical contact points required for minimal junction resistance. For systems operating at lower power levels, reduced compression forces may prove adequate while extending gasket service life, but insertion loss performance should be verified through network analyzer measurements to confirm that reduced torque values deliver acceptable electrical performance.
Frequency-Dependent Performance Characteristics of Waveguide Flange Gasket Materials
The electrical performance of Waveguide Flange Gasket materials exhibits frequency-dependent behavior driven by fundamental electromagnetic phenomena including skin effect, proximity effect, and the frequency response of conductive particle networks within elastomer matrices. Engineers designing systems operating across wide frequency ranges from L-band through W-band must understand how gasket material properties interact with frequency to optimize material selection for specific applications. While high-quality conductive elastomers maintain excellent performance across frequencies extending to 110 GHz, subtle performance variations occur that can impact system design decisions for particularly demanding applications. Skin effect, which concentrates alternating currents increasingly near conductor surfaces as frequency increases, fundamentally affects current distribution through Waveguide Flange Gasket materials at microwave frequencies. At frequencies above 10 GHz, effective current penetration depth drops below 1 micrometer in silver conductors, meaning that electromagnetic energy interacts primarily with particle surfaces rather than particle bulk. Silver-filled and silver-plated materials prove particularly advantageous under these conditions because silver's low surface resistance minimizes losses even when current flow concentrates in very thin surface layers. The numerous particle-to-particle contact points throughout the gasket thickness ensure that multiple low-resistance current paths remain available even as skin effect forces currents toward surfaces.
Particle loading percentage and particle size distribution influence frequency response characteristics through their effects on the number and quality of conductive pathways through the elastomer matrix. Higher silver content formulations with 80-85% metal loading create more numerous inter-particle contacts, reducing the average number of metal-polymer-metal junctions that electrons must traverse when crossing the gasket thickness. This increased pathway redundancy proves particularly beneficial at millimeter-wave frequencies where even small contact resistances can generate measurable insertion loss. Advanced Waveguide Flange Gasket formulations utilize multi-modal particle size distributions combining several different particle size ranges, which allows smaller particles to fill gaps between larger particles and creates more efficient packing that maximizes conductive pathway density.
Temperature Effects on Insertion Loss Performance
Waveguide systems frequently operate across extreme temperature ranges that significantly affect both Waveguide Flange Gasket material properties and overall system insertion loss characteristics. Aerospace applications may experience temperatures from -55°C during high-altitude flight to +85°C on sun-exposed external surfaces, while high-power transmission systems can see localized temperatures exceeding +125°C near waveguide junctions under full power operation. Conductive elastomer materials must maintain stable electrical and mechanical properties throughout these temperature excursions to ensure consistent low insertion loss performance regardless of environmental conditions. Thermal expansion coefficient matching between gasket materials, waveguide metals, and flange materials influences junction stability across temperature cycles. Aluminum waveguide components exhibit thermal expansion coefficients near 23 ppm/°C, while silicone elastomers typically expand at 200-300 ppm/°C—an order of magnitude higher. This expansion mismatch means that gasket dimensions change significantly more than flange dimensions during temperature excursions, potentially altering contact pressure distribution and electrical contact quality. High-quality Waveguide Flange Gasket designs account for this differential expansion through gasket geometry and compression specifications that maintain adequate contact pressure across the full operational temperature range despite dimension changes.
Electrical conductivity of conductive elastomer materials exhibits temperature dependence related to thermal expansion of the polymer matrix and thermal effects on inter-particle contact resistance. As temperature increases, the silicone polymer expands and becomes more compliant, potentially reducing inter-particle contact forces and slightly increasing junction resistance between metal particles. However, this effect remains modest in properly formulated materials, with typical conductivity decreasing by less than 20% over a -55°C to +125°C temperature range. More significantly, temperature cycling can gradually degrade contact quality if the gasket material exhibits creep or stress relaxation, making materials with expanded metal reinforcement essential for applications experiencing frequent or severe thermal cycling. These reinforced formulations maintain contact pressure and electrical performance through thousands of thermal cycles that would cause unreinforced materials to relax and lose contact pressure.
Material Selection Guidelines for Specific Applications
Selecting optimal Waveguide Flange Gasket materials requires balancing multiple performance parameters including insertion loss, environmental sealing capability, temperature range, frequency coverage, power handling, and service life expectations against application-specific requirements and constraints. Different applications emphasize different performance aspects—satellite communication ground stations prioritize long-term outdoor durability and low insertion loss, aerospace radar systems demand wide temperature operation and vibration resistance, while laboratory test systems value reusability and ease of installation. Understanding these application-specific priorities enables informed material selection that delivers optimal performance for each unique requirement set. Telecommunications and satellite communication applications demand gasket materials delivering exceptionally low insertion loss to maximize signal-to-noise ratios and link margins in systems where received signal power levels may reach only picowatts. Every 0.01 dB of insertion loss at critical system interfaces translates directly to reduced system margin that must be compensated through higher transmit power, larger antennas, or reduced data rates. For these demanding applications, silver-filled silicone Waveguide Flange Gasket materials with the highest available conductivity prove essential, even at premium costs. Environmental durability becomes equally critical for outdoor installations experiencing decades of exposure to temperature extremes, humidity, solar radiation, and atmospheric contaminants. Materials must resist UV degradation, oxidation, and biological attack while maintaining stable electrical properties throughout 20-30 year service lives typical of satellite earth station equipment.
Defense and aerospace radar systems present unique challenges combining wide operational temperature ranges, high vibration and shock loads, and requirements for consistent performance across mission-critical applications. Aircraft-mounted radar systems experience temperatures from -55°C at altitude to +85°C on the flight line, with rapid thermal transitions during climb and descent profiles. Simultaneously, these systems endure vibration spectra from engine operation, aerodynamic buffeting, and landing impacts that can fatigue or dislodge poorly secured gasket installations. Waveguide Flange Gasket materials for these applications must deliver reliable performance across extreme environments while maintaining dimensional stability and contact pressure under sustained vibration exposure. Silver-filled silicone formulations with expanded metal reinforcement provide the necessary combination of electrical performance, environmental resistance, and mechanical durability, with molded O-ring and D-ring profiles proving optimal for secure installation in grooved flange configurations.
OEM Customization Options for Specialized Requirements
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd. recognizes that standard Waveguide Flange Gasket configurations cannot address every application requirement, offering comprehensive OEM services to develop customized solutions for specialized dimensions, unique frequency ranges, or unusual environmental conditions. Custom gasket development begins with detailed consultation between our applications engineering team and the customer's design engineers to fully understand system requirements, performance objectives, environmental constraints, and any unique challenges presented by the specific application. This collaborative approach ensures that custom designs address actual application needs rather than assumed requirements. Material customization represents one dimension of OEM capability, with options extending beyond standard silver-filled and silver-plated copper formulations to include alternative filler materials, polymer matrices optimized for specific temperature ranges, or specialized formulations providing enhanced chemical resistance for applications involving exposure to fuels, solvents, or cleaning agents. For outdoor telecommunications applications in tropical environments, materials incorporating additional UV stabilizers and biocidal additives deliver extended service life compared to standard formulations. Ultra-high vacuum applications may require materials specifically formulated for minimal outgassing, utilizing platinum-cured silicones and carefully selected fillers that maintain conductivity while meeting stringent vacuum compatibility requirements.
Dimensional customization addresses non-standard waveguide sizes, double-ridged waveguide configurations, or unusual flange geometries not covered by industry standard specifications. Our precision die-cutting capabilities produce flat Waveguide Flange Gasket configurations from sheet stock materials in virtually any two-dimensional geometry, while molding operations can create O-ring and D-ring profiles in custom cross-sections and diameters matched to unique groove dimensions. Engineering support includes finite element analysis of gasket compression behavior, thermal modeling of temperature distribution in high-power applications, and electromagnetic simulation of junction performance to optimize gasket geometry for minimal insertion loss. This comprehensive technical support ensures that custom gasket designs deliver reliable performance meeting or exceeding application requirements while minimizing development time and risk.
Conclusion
Achieving minimal insertion loss in waveguide systems fundamentally depends on selecting high-conductivity Waveguide Flange Gasket materials such as silver-filled silicone and silver-plated copper formulations, combined with proper installation practices and application-appropriate gasket configurations. Material properties, flange compatibility, and environmental conditions must align to ensure optimal electromagnetic performance and long-term reliability across diverse telecommunications, aerospace, and defense applications.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Partner with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd., a leading China Waveguide Flange Gasket manufacturer with over 20 years of microwave expertise. As a trusted China Waveguide Flange Gasket supplier and China Waveguide Flange Gasket factory, we offer High Quality Waveguide Flange Gasket solutions with competitive Waveguide Flange Gasket price. Our extensive Waveguide Flange Gasket for sale includes both standard and OEM configurations, supported by ISO certifications, advanced 110 GHz testing facilities, and expert technical guidance. Whether you need China Waveguide Flange Gasket wholesale solutions or customized designs, our team delivers fast turnaround, rigorous quality control, and comprehensive after-sales support. Contact craig@admicrowave.com today to discuss your requirements and discover how our waveguide components can optimize your system performance. Bookmark this resource for future reference as your waveguide technology challenges evolve.
References
1. Bahl, I. J., & Bhartia, P. (2003). Microwave Solid State Circuit Design (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
2. Montgomery, C. G., Dicke, R. H., & Purcell, E. M. (Eds.). (1948). Principles of Microwave Circuits. MIT Radiation Laboratory Series, McGraw-Hill.
3. Saad, T. S. (Ed.). (1971). Microwave Engineers' Handbook (Volumes 1 & 2). Artech House.
4. Clarricoats, P. J. B., & Olver, A. D. (1984). Corrugated Horns for Microwave Antennas. IEE Electromagnetic Waves Series, Peter Peregrinus Ltd.
5. Harvey, A. F. (1963). Microwave Engineering. Academic Press.
YOU MAY LIKE
 VIEW MOREHigh Power Waveguide to Coaxial Adapter
VIEW MOREHigh Power Waveguide to Coaxial Adapter VIEW MOREWaveguide Loop Coupler
VIEW MOREWaveguide Loop Coupler VIEW MOREEnd Launch Double Ridged WG To Coaxial Adapter
VIEW MOREEnd Launch Double Ridged WG To Coaxial Adapter VIEW MOREEnd Launch Waveguide to Microstrip Adapter
VIEW MOREEnd Launch Waveguide to Microstrip Adapter VIEW MOREWaveguide Sliding Termination
VIEW MOREWaveguide Sliding Termination VIEW MOREWaveguide Unmatched Termination
VIEW MOREWaveguide Unmatched Termination VIEW MOREMagic Hybrid Tee
VIEW MOREMagic Hybrid Tee VIEW MOREH-Plane Tee
VIEW MOREH-Plane Tee




