Are Elliptical Waveguide Antennas Better for Narrow Beams?
Imagine your satellite ground station struggling to maintain a stable connection during critical data transmission, or your radar system failing to distinguish between closely spaced targets in high-density environments. These aren't hypothetical scenarios—they're the daily challenges faced by engineers working with high-frequency microwave systems. The answer to whether Elliptical Waveguide antennas deliver superior narrow beam performance lies in understanding their unique electromagnetic properties and how their geometry fundamentally shapes signal propagation, offering significantly enhanced directivity and precision compared to traditional circular or rectangular waveguide configurations in applications demanding ultra-narrow beamwidths.
Understanding Elliptical Waveguide Fundamentals and Beam Formation Principles
Elliptical Waveguide technology represents a sophisticated evolution in microwave transmission systems, designed specifically to address the demanding requirements of narrow beam applications. The elliptical cross-sectional geometry creates distinct electromagnetic field distributions that directly influence beamwidth characteristics and directivity patterns. Unlike circular waveguides that produce symmetrical radiation patterns, or rectangular waveguides constrained by their aspect ratios, Elliptical Waveguide structures enable precise control over beam shape through their adjustable major and minor axis dimensions. This fundamental geometric advantage allows engineers to tailor radiation patterns for specific applications requiring asymmetrical beam characteristics, particularly valuable in scenarios where coverage must be optimized in one plane while maintaining focus in another. The physical construction of Elliptical Waveguide typically involves an elliptical corrugated copper tube, which provides excellent electrical conductivity and structural integrity, wrapped in a UV-resistant black polyethylene jacket for environmental protection. This robust design ensures minimal signal degradation across extended frequency ranges, from sub-6 GHz bands up to millimeter-wave frequencies exceeding 110 GHz. The corrugated internal structure serves multiple purposes: it reduces mode conversion losses, minimizes dispersion effects, and maintains consistent impedance characteristics throughout the transmission path. When integrated into antenna systems, these waveguides function as critical feed elements that transform guided electromagnetic waves into precisely controlled radiation patterns, with the elliptical geometry enabling superior control over beam narrowing in specific planes.
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd specializes in manufacturing high-quality Elliptical Waveguide components that meet ISO 9001:2008 standards and RoHS compliance requirements. Our products are engineered with elliptical corrugated copper tubes and UV-resistant black polyethylene jackets, ensuring durability in challenging outdoor environments. With over twenty years of experience in microwave product development and a state-of-the-art 24-meter microwave darkroom capable of testing frequencies from 0.5 to 110 GHz, we provide comprehensive technical support for antenna designers seeking optimal narrow beam performance. Our manufacturing capabilities include custom waveguide designs tailored to specific frequency ranges, power handling requirements, and environmental conditions, supported by rigorous quality control procedures that verify every component meets or exceeds industry benchmarks.
How Elliptical Geometry Achieves Superior Narrow Beam Characteristics?
The relationship between waveguide cross-sectional shape and resultant beam characteristics stems from fundamental electromagnetic boundary conditions and modal field distributions. Elliptical Waveguide structures support unique propagation modes that differ significantly from those in rectangular or circular geometries. The elliptical shape creates asymmetric field distributions where electromagnetic energy concentrates differently along the major versus minor axes, enabling engineers to achieve narrow beamwidths in selected planes while maintaining desired coverage in perpendicular orientations. This capability proves invaluable in applications like air traffic control radar, where ultra-sharp beamforming along the elevation plane enhances aircraft tracking accuracy even during adverse weather conditions, while maintaining sufficient azimuthal coverage for area surveillance. The mathematical foundation governing Elliptical Waveguide performance involves complex elliptical coordinate solutions to Maxwell's equations, where modes are designated as HC (cosine-elliptic) and HS (sine-elliptic) rather than the TE and TM modes familiar in rectangular waveguides. The fundamental HC11 mode in elliptical structures exhibits field maxima distributed according to the ellipse geometry, creating natural focusing effects that concentrate electromagnetic energy into narrower angular distributions. As frequency increases within the operational bandwidth, the propagation constant shifts, causing beam pointing direction variations that can be leveraged for electronic scanning applications or must be compensated for in fixed-beam systems through careful design optimization.
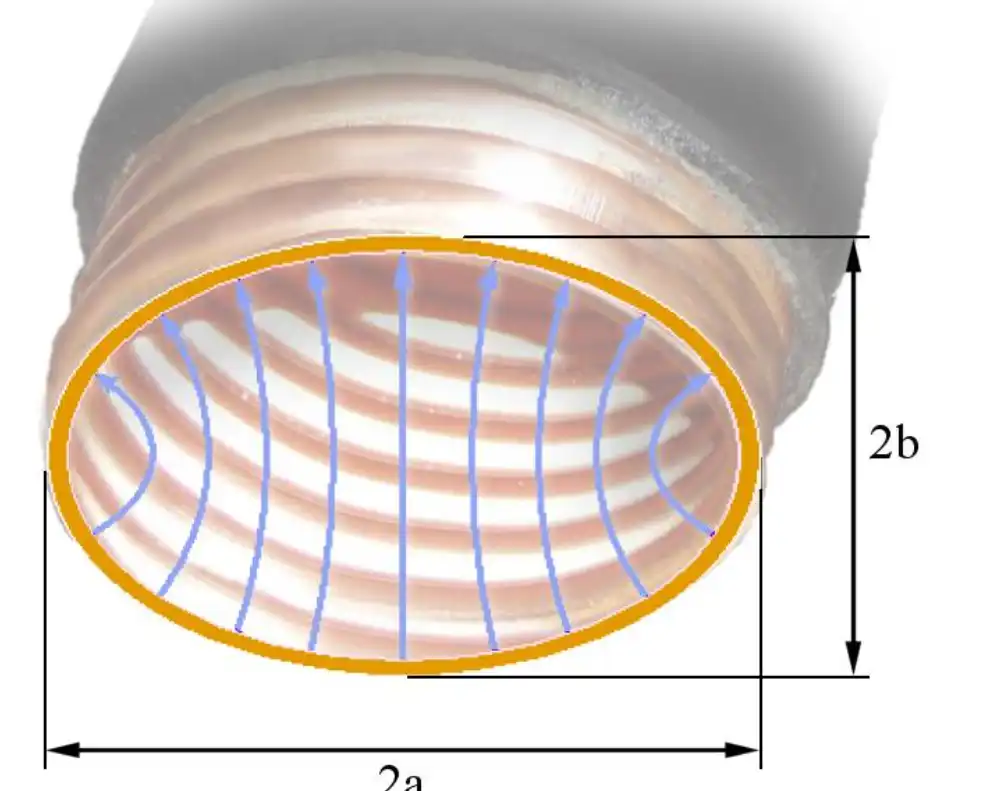
Beamwidth Control Through Dimensional Optimization
Precise control over narrow beam formation in Elliptical Waveguide antenna systems requires careful selection of the major-to-minor axis ratio, absolute dimensions relative to operating wavelength, and transition geometry between the waveguide and free space. Increasing the major axis dimension relative to wavelength naturally narrows the beamwidth in the plane perpendicular to that axis, following diffraction-limited principles where larger apertures produce tighter angular resolution. However, this relationship isn't linear—optimum performance requires balancing multiple factors including impedance matching, higher-order mode suppression, and maintaining acceptable sidelobe levels. Engineers designing narrow beam systems must conduct comprehensive electromagnetic simulations accounting for the complete feed network, including any tapers, mode converters, or polarization transformers required to interface Elliptical Waveguide components with antenna radiating elements. Our custom X-Band feed network capabilities at Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd demonstrate practical implementation of these principles, delivering ultra-sharp beamforming for accurate target discrimination in defense and aerospace applications. These networks integrate optimized Elliptical Waveguide sections with precision-machined flanges and couplers, ensuring minimal insertion loss and excellent phase stability across the operational bandwidth. The ability to customize waveguide dimensions, flange configurations, and material selections enables us to meet diverse customer requirements, from compact UAV-mounted systems requiring lightweight designs to high-power ground-based radar installations demanding robust thermal management. Our technical support team provides comprehensive assistance from initial specification development through installation and commissioning, ensuring seamless integration of Elliptical Waveguide components into complete antenna systems.
Comparative Performance Analysis: Elliptical Versus Alternative Waveguide Configurations
When evaluating waveguide technologies for narrow beam applications, system designers must consider multiple performance metrics beyond simple beamwidth specifications. Elliptical Waveguide offers distinct advantages in scenarios requiring asymmetrical radiation patterns, where conventional circular or rectangular waveguides would necessitate complex beam-forming networks or lossy transformation sections. The inherent asymmetry of the elliptical cross-section provides a direct path to asymmetric beam shaping without additional components, reducing system complexity, insertion loss, and overall cost while improving reliability through reduced component count. In satellite ground station applications, this translates to enhanced signal-to-noise ratios for both uplink and downlink paths, critical for maintaining stable connections under marginal atmospheric conditions or when operating near link budget limits. Rectangular waveguide systems, while offering excellent performance for many applications, typically generate symmetrical or near-symmetrical radiation patterns determined by the standard aspect ratios dictated by cutoff frequency requirements. Achieving narrow beams in one plane while maintaining broader coverage in the orthogonal plane requires either mechanical aperture shaping through horn flare angles or electrical beam-forming using array techniques—both approaches adding complexity and potential loss mechanisms. Circular waveguide, although providing lowest transmission loss per unit length and excellent power handling capacity, produces purely symmetrical patterns unsuitable for applications requiring deliberate asymmetry. The Elliptical Waveguide approach combines favorable aspects of both geometries: low loss comparable to circular waveguide in one dimension, pattern control flexibility approaching that of rectangular systems, and unique asymmetric capabilities unavailable in either conventional configuration.
Application-Specific Performance Optimization
Different narrow beam applications impose varying requirements on waveguide selection and system architecture. Weather monitoring radar systems demand extremely narrow elevation beams to achieve fine altitude resolution for precipitation profiling, while maintaining broader azimuthal coverage for area surveillance—an ideal match for Elliptical Waveguide feed architectures. Shipboard communication systems face unique challenges including limited installation space, severe environmental exposure, and requirements for beam steering or switching between multiple coverage zones; here, the compact cross-section and flexible routing capabilities of Elliptical Waveguide offer significant installation advantages over rigid rectangular alternatives. Direction-finding applications benefit from the precise phase control achievable in well-designed Elliptical Waveguide distribution networks, where maintaining phase balance across multiple receiving channels proves critical for accurate angle-of-arrival determination. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd addresses these diverse requirements through comprehensive customization services covering waveguide dimensions, flange types, material selections, and specialized features like integrated pressure windows or mode filters. Our engineering team works closely with customers to understand specific application constraints, conducting detailed electromagnetic analyses to optimize Elliptical Waveguide parameters for target performance specifications. Whether your project demands ultra-low insertion loss for long cable runs, exceptional power handling for transmit applications, or stringent phase tracking for interferometric systems, we provide tailored solutions backed by rigorous testing in our ISO-certified laboratories. The combination of advanced simulation capabilities, precision manufacturing, and comprehensive measurement facilities ensures delivered products meet or exceed specified performance across all relevant parameters.
Technical Implementation Considerations for Elliptical Waveguide Narrow Beam Systems
Successful deployment of Elliptical Waveguide in narrow beam antenna systems requires attention to numerous technical details beyond basic waveguide specification. Interface transitions between Elliptical Waveguide and other system components—whether rectangular waveguide, coaxial transmission lines, or directly to radiating elements—must be carefully designed to minimize mismatch losses and avoid exciting unwanted modes that could degrade beam quality. Mode purity throughout the entire transmission path proves essential for maintaining narrow beam integrity; any asymmetric perturbations or discontinuities can couple energy into higher-order modes exhibiting different propagation velocities and radiation characteristics, potentially distorting the desired pattern or reducing directivity. Proper installation practices including precise alignment, appropriate support spacing to prevent mechanical deformation, and environmental sealing to exclude moisture all contribute to long-term performance stability. The frequency-dependent behavior of Elliptical Waveguide systems necessitates careful bandwidth planning for applications requiring consistent beam characteristics across wide frequency ranges. As operating frequency varies, both the effective aperture size in wavelengths and the dominant mode field distribution shift, causing beam pointing variations and beamwidth changes that may or may not be acceptable depending on system requirements. Broadband systems spanning octave or wider bandwidths may require compensating elements or acceptance of performance variations across the tuning range. Advanced design techniques including corrugated waveguide sections, dielectric loading, or carefully engineered transitions can extend useful bandwidth while maintaining acceptable beam parameter stability, though often at the cost of increased complexity and manufacturing precision requirements.
Integration with Modern Measurement and Verification Capabilities
Verifying that Elliptical Waveguide antenna systems achieve specified narrow beam performance requires sophisticated measurement facilities capable of accurate far-field characterization across the operational frequency range. Our 24-meter microwave darkroom at Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd provides the precise measurement distance necessary for evaluating antenna far-field behavior up to 110 GHz, well beyond the capabilities of typical compact ranges. The Antenna Plane Near and Far Field Measuring Recombination Chamber serves as the technical centerpiece, enabling our team to conduct both near-field scanning for detailed aperture diagnostics and true far-field measurements for pattern verification. This dual capability proves invaluable when optimizing Elliptical Waveguide feed networks, allowing direct correlation between measured field distributions and predicted electromagnetic simulations, identifying any manufacturing variations or assembly issues requiring correction. Pattern measurements reveal critical performance parameters including main beam direction, 3dB beamwidth in principal planes, sidelobe levels, cross-polarization characteristics, and gain across the frequency band. For narrow beam systems, these measurements must be conducted with angular resolution fine enough to accurately characterize the sharp pattern features, requiring precision positioning systems and calibrated measurement antennas appropriate for the frequency range. Our measurement protocols follow strict procedures ensuring reliable, repeatable results that customers can confidently use for system integration decisions. The data obtained during factory acceptance testing provides baseline performance documentation that enables end-users to verify proper installation and ongoing operational performance through periodic field measurements.
Conclusion
Elliptical Waveguide antennas demonstrate clear advantages for narrow beam applications through geometric control, reduced complexity, and superior pattern shaping compared to conventional alternatives.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd stands ready as your trusted China Elliptical Waveguide manufacturer, China Elliptical Waveguide supplier, and China Elliptical Waveguide factory, offering China Elliptical Waveguide wholesale solutions and High Quality Elliptical Waveguide for sale at competitive Elliptical Waveguide price points. With over twenty years of microwave expertise, ISO certification, and state-of-the-art testing facilities including our 24-meter darkroom supporting frequencies to 110 GHz, we deliver customized waveguide assemblies, rapid prototyping, comprehensive technical support, and global logistics ensuring fast delivery worldwide. Contact craig@admicrowave.com today to discuss your narrow beam antenna requirements and discover how our OEM services can optimize your next project.
References
1. Bhardwaj, S., & Volakis, J. L. (2018). Hexagonal Waveguide Based Circularly Polarized Horn Antennas for Sub-mm-Wave/Terahertz Band. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation.
2. Doane, J. L. (1986). Polarization Converters for Circular Waveguide Modes. International Journal of Electronics.
3. Yu, Z., Chen, J., & Wang, X. (2019). A Circularly Polarized Horn Antenna with Elliptical Waveguide Polarizer. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters.
4. Stange, T. (2015). Simple Broadband Circular Polarizer in Oversized Waveguide. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves.
5. Perron, A., Denidni, T. A., & Sebak, A. R. (2010). Circularly Polarized Microstrip/Elliptical Dielectric Ring Resonator Antenna for Millimeter-Wave Applications. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters.
YOU MAY LIKE
 VIEW MORELog Periodic Antenna
VIEW MORELog Periodic Antenna VIEW MORESlotted Waveguide Array Antenna
VIEW MORESlotted Waveguide Array Antenna VIEW MOREOpen Boundary Dual Linear Polarization Four Ridged Horn Antenna
VIEW MOREOpen Boundary Dual Linear Polarization Four Ridged Horn Antenna VIEW MOREConical Dual circular Polarization Horn Antenna
VIEW MOREConical Dual circular Polarization Horn Antenna VIEW MORELadder Membrane Conical Dual circular Polarization Horn Antenna
VIEW MORELadder Membrane Conical Dual circular Polarization Horn Antenna VIEW MOREDual Linear Broadband Dual Circular Polarization Horn Antenna
VIEW MOREDual Linear Broadband Dual Circular Polarization Horn Antenna VIEW MOREConical Linear Polarization Horn Antenna
VIEW MOREConical Linear Polarization Horn Antenna VIEW MOREPlanar Spiral Antenna
VIEW MOREPlanar Spiral Antenna




