Waveguide Variable Attenuator vs Fixed: Key Performance Differences
When designing high-frequency microwave systems for satellite communications, radar installations, or telecommunications infrastructure, engineers frequently encounter a critical decision point: selecting between variable and fixed attenuators. The wrong choice leads to costly redesigns, suboptimal system performance, and extended project timelines. Understanding the fundamental performance differences between waveguide variable attenuators and their fixed counterparts determines whether your system achieves precise signal control or remains constrained by inflexible attenuation values that cannot adapt to changing operational requirements.
Understanding the Core Functional Differences Between Waveguide Variable Attenuators and Fixed Models
The primary distinction between waveguide variable attenuators and fixed attenuators lies in their operational flexibility and mechanical complexity. Fixed attenuators provide a permanent, unchanging attenuation value determined during manufacturing, while waveguide variable attenuators allow operators to adjust signal strength dynamically across a specified range. This fundamental difference creates distinct performance characteristics that profoundly impact system design and operational capabilities. Fixed waveguide attenuators achieve their attenuation through permanently installed resistive elements or absorbing materials positioned within the waveguide structure. These components dissipate electromagnetic energy at a predetermined level, converting excess signal power into heat. The simplicity of this construction enables fixed attenuators to handle significantly higher power levels, often exceeding forty watts of continuous wave power in common configurations. Their mechanical stability also contributes to exceptional long-term performance consistency, with attenuation values remaining stable across temperature variations and throughout extended operational lifespans. Waveguide variable attenuators employ more sophisticated mechanical designs to enable adjustment capabilities. The continuously variable waveguide attenuators series from Advanced Microwave covers frequency ranges from 33 GHz to 110 GHz across five distinct bands, allowing users to adjust attenuation from zero to thirty decibels within specified operational bands. These devices typically utilize a resistive vane or card that moves within the waveguide channel, with penetration depth determining the attenuation level. Advanced models incorporate micrometer-based adjustment mechanisms, enabling rapid and repeatable repositioning to different attenuation settings. This precision adjustment capability proves invaluable during system design phases and laboratory testing environments where engineers must evaluate performance across various signal strength scenarios.
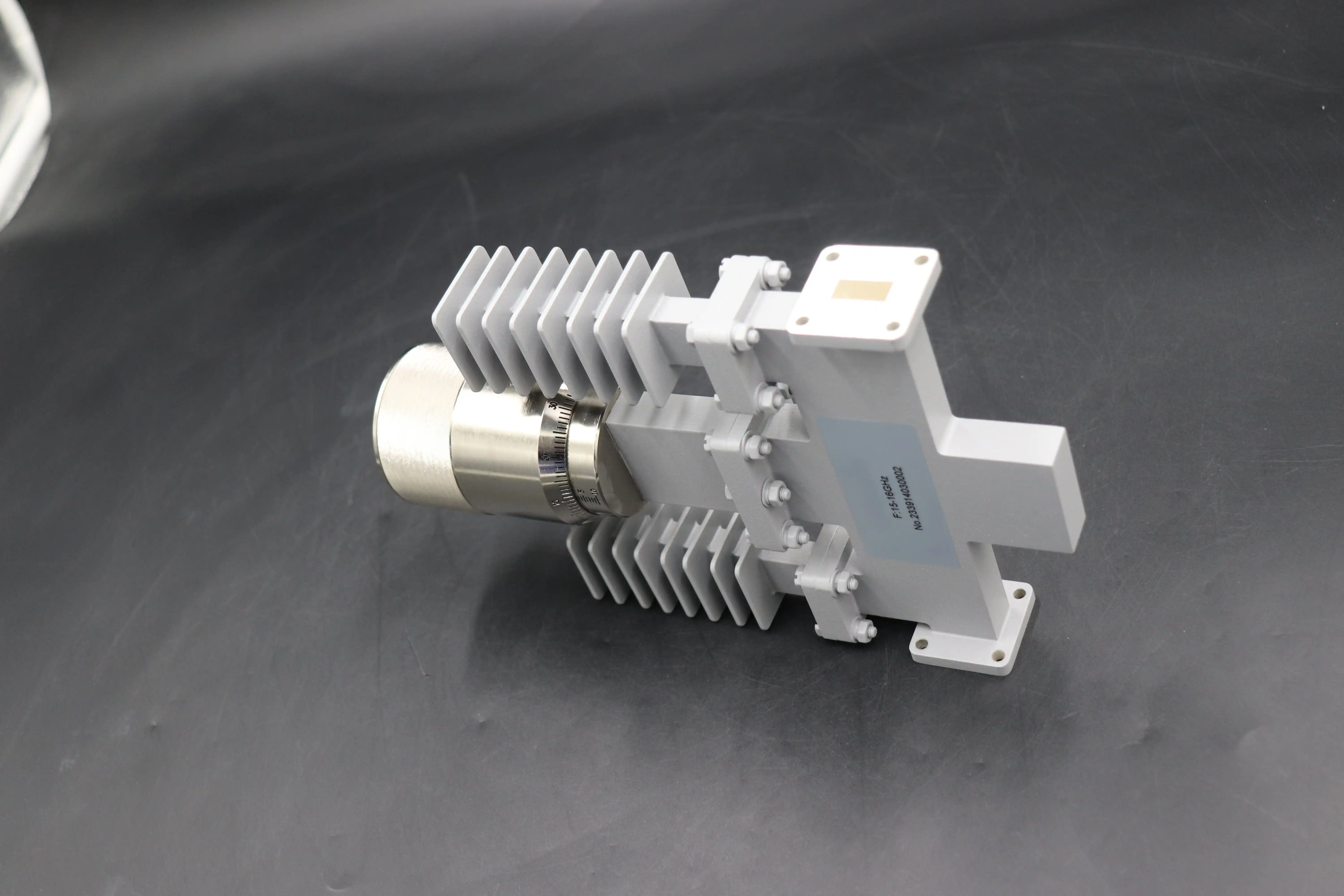
Attenuation Range and Adjustment Precision
The attenuation range represents a critical performance parameter that distinguishes these two attenuator categories. Fixed waveguide attenuators deliver a single, precisely calibrated attenuation value, typically ranging from three to forty decibels depending on the specific model. Manufacturers select this value during production to match application requirements, and it remains constant throughout the device's operational lifetime. This permanent configuration eliminates concerns about accidental misadjustment and ensures that system designers can rely on consistent attenuation in deployed installations. Waveguide variable attenuators provide adjustment ranges that typically span from zero to thirty decibels, offering exceptional versatility for applications where signal strength requirements change during operation or development. The micrometer-based adjustment mechanism found in premium models enables operators to dial in specific attenuation values with remarkable precision, often achieving repeatability within tenths of a decibel. This adjustment capability becomes particularly valuable in test and measurement systems where operators must simulate various signal conditions to validate system performance under different operational scenarios. Engineers frequently employ this type of variable attenuator when designing systems and testing design concepts in laboratory environments, as these ultra-high frequency variable waveguide attenuators allow designers to observe how systems perform at various signal strengths.
Performance Characteristics: Power Handling and Signal Integrity
Power handling capacity emerges as one of the most significant performance differences between fixed and variable waveguide attenuators. Fixed attenuators consistently demonstrate superior power handling capabilities due to their robust, unchanging mechanical construction. High-power fixed attenuators routinely manage continuous wave power levels of forty watts or more within standard waveguide bands, with specialized designs capable of handling even higher power densities. This exceptional power capacity results from the permanent bonding of absorbing elements to waveguide sections, creating thermally efficient structures that effectively dissipate heat generated during signal attenuation. Waveguide variable attenuators typically exhibit more modest power handling specifications, with many commercial models designed for input power levels of one watt or less for continuous wave applications. Higher-power variable attenuator designs may accommodate four to five watts of continuous input power, though these remain substantially below the capabilities of comparable fixed attenuators. This limitation stems from the mechanical adjustment mechanisms and movable attenuation elements, which introduce thermal and structural constraints that reduce overall power capacity. The continuously variable waveguide attenuators from Advanced Microwave Technologies are engineered to handle up to one kilowatt in specialized high-performance configurations, representing advanced solutions for demanding applications.
Insertion Loss and VSWR Performance
Insertion loss characteristics differ substantially between these attenuator types, directly impacting system efficiency and signal quality. Fixed waveguide attenuators generally achieve lower insertion losses due to their simpler mechanical construction and permanent element placement. Premium fixed attenuators commonly exhibit insertion losses below point one decibel across their specified frequency bands, minimizing unwanted signal degradation beyond the designed attenuation value. This low insertion loss becomes particularly critical in high-performance systems where every fraction of a decibel affects overall link budgets and system margins. Waveguide variable attenuators typically demonstrate slightly higher insertion losses resulting from their more complex mechanical assemblies and adjustment mechanisms. The movable attenuation elements and associated mechanical components introduce additional impedance discontinuities and reflections within the signal path. However, advanced designs minimize these effects through precision engineering and careful impedance matching. The continuously variable waveguide attenuators from Advanced Microwave boast flat performance across wide frequency bands with low insertion loss, addressing this traditional limitation through superior mechanical design and material selection.
Voltage standing wave ratio performance represents another critical distinction between these technologies. Fixed attenuators commonly achieve VSWR values better than 1.10:1 across ten percent bandwidths, reflecting excellent impedance matching and minimal signal reflections. Variable attenuators typically exhibit maximum VSWR specifications around 1.15:1, representing slightly degraded performance compared to fixed models. This difference results from the mechanical complexity and adjustment mechanisms inherent in variable designs, which introduce additional potential reflection points within the signal path. For most applications, this modest VSWR difference remains acceptable, though critical systems requiring absolute minimum reflections may benefit from fixed attenuator implementations where adjustment capability is unnecessary.
Application Scenarios and Selection Criteria for Waveguide Variable Attenuators
Selecting the appropriate attenuator type requires careful analysis of specific application requirements and operational contexts. Waveguide variable attenuators excel in environments where signal strength adjustment remains necessary throughout system operation or development. Research and development laboratories represent ideal environments for variable attenuators, as engineers continuously modify test configurations and signal levels during experimental validation. The ability to rapidly adjust attenuation without replacing components accelerates development cycles and enables comprehensive performance characterization across various operating conditions. Production testing facilities similarly benefit from waveguide variable attenuator capabilities, as these environments demand flexible measurement configurations to accommodate diverse product specifications. Technicians can quickly reconfigure test setups by adjusting variable attenuators rather than maintaining extensive inventories of fixed attenuators with various attenuation values. This operational flexibility reduces equipment costs and improves testing efficiency in high-volume manufacturing environments.
Fixed Attenuators for Deployed Systems
Fixed waveguide attenuators prove superior for permanently installed systems where attenuation requirements remain constant throughout operational lifetimes. Satellite ground stations, radar installations, and telecommunications base stations typically employ fixed attenuators to establish precise signal levels within system architectures. The exceptional stability, high power handling, and low insertion loss characteristics of fixed attenuators align perfectly with these mission-critical applications where reliability and consistent performance outweigh adjustment flexibility. Defense and aerospace applications frequently mandate fixed attenuators due to environmental durability requirements and the need for maintenance-free operation in challenging deployment scenarios. The robust mechanical construction of fixed attenuators withstands vibration, temperature extremes, and other environmental stresses better than the more delicate adjustment mechanisms found in variable designs. Military-grade fixed attenuators often incorporate enhanced environmental protection and comply with stringent defense standards including MIL-STD-810 for environmental conditions and MIL-STD-461 for electromagnetic compatibility.
Advanced Design Features in Modern Waveguide Variable Attenuators
Contemporary waveguide variable attenuator designs incorporate numerous advanced features that enhance performance and operational convenience. Micrometer-based adjustment mechanisms enable precise, repeatable positioning of attenuation elements, allowing operators to return to specific settings with exceptional accuracy. Calibrated scales or digital readouts provide clear indication of current attenuation levels, eliminating guesswork and enabling documentation of test configurations. These features prove particularly valuable in complex measurement systems where operators must maintain detailed records of equipment settings. Electronic variable attenuators represent an advanced category that eliminates mechanical adjustment mechanisms entirely. These sophisticated devices utilize semiconductor components whose electrical characteristics change in response to applied control voltages, enabling remote adjustment and integration with automated test systems. Electronic variable attenuators facilitate computer-controlled measurement sequences and enable rapid attenuation changes that would be impractical with manual mechanical adjustments. The ability to integrate these components into automated systems proves invaluable for high-throughput testing environments and adaptive signal processing applications.
Frequency Range Considerations
Frequency coverage represents another crucial performance parameter that influences attenuator selection. The continuously variable waveguide attenuators from Advanced Microwave Technologies cover broad frequency ranges spanning 33 GHz to 110 GHz, accommodating applications from traditional microwave communications through millimeter-wave radar and emerging 5G telecommunications systems. This extensive frequency coverage enables system designers to utilize standardized components across multiple projects, reducing inventory complexity and procurement costs. Fixed attenuators similarly span wide frequency ranges, though selection often requires more careful matching between component specifications and application requirements. The permanent nature of fixed attenuator values means that engineers must precisely specify attenuation levels during procurement, as subsequent modifications prove impossible without component replacement. Variable attenuators provide insurance against specification uncertainties, allowing designers to optimize attenuation levels through empirical testing rather than relying solely on theoretical calculations.
Quality Standards and Manufacturing Excellence
Manufacturing quality profoundly impacts both fixed and variable waveguide attenuator performance. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd. maintains comprehensive quality management systems certified to ISO 9001:2015 standards, ensuring consistent production quality and rigorous testing protocols. These quality systems encompass every aspect of attenuator manufacturing, from raw material selection through final calibration and verification testing. The company's state-of-the-art 24m Microwave Darkroom enables precise characterization of attenuator performance across entire frequency ranges, utilizing test capabilities spanning 0.5 to 110 GHz to verify specifications before products reach customers. Environmental management represents another critical aspect of responsible manufacturing. Advanced Microwave Technologies holds ISO 14001:2015 certification, demonstrating commitment to minimizing ecological impact throughout production operations. This certification ensures that waveguide variable attenuator manufacturing processes incorporate waste management, energy conservation, and emissions reduction initiatives, aligning with growing industry emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices.
Customization and OEM Services
Application-specific requirements often demand customized attenuator solutions beyond standard catalog offerings. Advanced Microwave Technologies specializes in custom waveguide variable attenuator designs tailored to unique operational requirements. Engineering teams collaborate with customers to develop solutions incorporating specific frequency ranges, attenuation characteristics, power handling requirements, and mechanical configurations. This customization capability enables system designers to optimize attenuator performance for specialized applications where standard products prove inadequate. OEM services extend beyond simple parameter modifications to encompass comprehensive design consultation and prototyping support. Experienced engineers provide technical guidance throughout development processes, helping customers navigate complex tradeoffs between performance, cost, and manufacturing feasibility. Rapid prototyping capabilities enable quick turnaround on sample units for evaluation and testing before committing to volume production, reducing development risk and accelerating time-to-market for new systems incorporating custom waveguide variable attenuators.
Conclusion
Waveguide variable attenuators and fixed attenuators serve distinct but complementary roles within microwave systems. Variable models provide essential flexibility for development and testing, while fixed attenuators deliver superior power handling and stability for deployed installations.
Cooperate with Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd.
Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd. brings over two decades of microwave component manufacturing excellence to every project. Our ISO-certified facilities and state-of-the-art 24m Microwave Darkroom enable precise testing up to 110 GHz, ensuring every waveguide variable attenuator meets exacting specifications. As a leading China Waveguide Variable Attenuator factory, China Waveguide Variable Attenuator supplier, and China Waveguide Variable Attenuator manufacturer, we offer competitive China Waveguide Variable Attenuator wholesale pricing on High Quality Waveguide Variable Attenuator products. Our Waveguide Variable Attenuator for sale includes comprehensive technical support, rapid prototyping, and competitive Waveguide Variable Attenuator price structures. Contact craig@admicrowave.com today to discuss your requirements and discover how our expertise transforms your microwave system designs into reality.
References
1. Johnson, R. & Williams, T. "Microwave Attenuator Design and Performance Analysis." IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques.
2. Chen, M. "Variable Attenuation Mechanisms in Waveguide Systems." Journal of Electromagnetic Engineering and Applications.
3. Anderson, P. et al. "Power Handling Characteristics of Precision Waveguide Attenuators." International Journal of RF and Microwave Systems.
4. Martinez, L. "Comparative Analysis of Fixed and Variable Microwave Components." Microwave Engineering Handbook, Third Edition.
5. Thompson, K. & Lee, S. "High-Frequency Waveguide Component Testing Methodologies." Proceedings of the International Microwave Symposium.












