What are the unique structural advantages of circular straight waveguides compared to rectangular ones?
When it comes to electromagnetic wave transmission in high-frequency applications, the structure of a waveguide plays a critical role in determining signal integrity and performance. Circular Straight Waveguide designs offer several distinct structural advantages over their rectangular counterparts. These cylindrical metallic structures provide superior electromagnetic field distribution, better power handling capabilities, and reduced signal degradation across a wide frequency spectrum. The unique circular cross-section facilitates more efficient propagation of certain wave modes while minimizing losses in critical telecommunications, defense, and aerospace applications.
Fundamental Structural Benefits of Circular Waveguides
Superior Mode Propagation Characteristics
Circular Straight Waveguide configurations provide exceptional mode propagation capabilities that rectangular waveguides cannot match. The symmetrical geometry of a circular waveguide allows for the propagation of transverse electric (TE) and transverse magnetic (TM) modes with rotational symmetry. This structural feature enables more predictable field patterns and more efficient transmission of circular polarized waves. When electromagnetic waves travel through a Circular Straight Waveguide, the field distribution maintains its integrity much better due to the absence of sharp corners where field concentration can lead to power losses and potential breakdown. Advanced Microwave Technologies leverages this fundamental advantage in their precision-engineered waveguides, which operate across an impressive frequency range from 1 GHz to 110 GHz. This wide operational bandwidth makes circular waveguides particularly valuable in satellite communications where signal integrity must be maintained across long transmission distances. The uniform inner surface of circular waveguides minimizes impedance variations that could otherwise cause reflections and standing waves, resulting in cleaner signal transmission especially in high-power applications where signal distortion must be minimized.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Pressure Handling
The circular cross-section of a Circular Straight Waveguide provides inherent structural integrity that rectangular designs cannot match. This geometric advantage translates to superior performance under mechanical stress and pressure differentials. Unlike rectangular waveguides that have flat surfaces prone to deformation, circular waveguides distribute external forces evenly across their structure. This makes them particularly suitable for aerospace and defense applications where equipment may be subjected to extreme conditions. Advanced Microwave's circular waveguides are manufactured using premium materials including aluminum, copper, or brass, further enhancing their durability and performance under challenging environments. The structural robustness of these waveguides means they maintain precise dimensional tolerances even when exposed to thermal cycling or physical stress. This is critical for maintaining consistent electrical performance over time. Additionally, circular waveguides exhibit better resistance to torsional forces, which prevents twisting that could distort the electromagnetic field inside the waveguide. Their pressure-handling capability makes them ideal for pressurized systems where signal integrity must be maintained despite environmental variations. This superior mechanical strength translates directly to longer operational lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements in complex systems where replacement would be costly or impractical.
Lower Attenuation at Higher Frequencies
One of the most significant structural advantages of Circular Straight Waveguide systems is their lower attenuation characteristics at higher frequencies compared to rectangular counterparts. The smooth, continuous inner surface minimizes skin effect losses, particularly important as frequencies increase. This characteristic makes circular waveguides particularly valuable for millimeter-wave applications where signal preservation is paramount. Advanced Microwave's circular waveguides feature high-quality surface finishes with conductive gold or silver plating that further reduces resistive losses. The circular geometry creates a more favorable ratio of surface area to cross-sectional area, which directly impacts attenuation. When electromagnetic waves propagate through these waveguides, they encounter less resistance, allowing signals to travel further distances without significant degradation. This advantage becomes increasingly important in long-distance transmission systems like satellite communications infrastructure. Additionally, the circular cross-section minimizes the effects of manufacturing imperfections on signal propagation. Even minor irregularities in rectangular waveguides can create localized impedance mismatches, while circular geometries tend to average out such effects. For applications requiring minimal insertion loss, such as precision measurement systems or high-sensitivity receivers, Advanced Microwave's circular waveguides with their VSWR ratings of ≤1.20:1 ensure signal fidelity is maintained throughout the transmission path. This performance advantage is why circular waveguides remain the preferred choice for many high-frequency, low-loss applications despite potentially higher manufacturing complexity.

Applications Leveraging Circular Waveguide Advantages
Satellite Communications Systems
Circular Straight Waveguide technology has become a cornerstone in modern satellite communication systems, where its unique structural advantages directly translate to performance benefits. The rotational symmetry of circular waveguides makes them ideal for handling circularly polarized signals commonly used in satellite communications to mitigate atmospheric effects and multipath interference. Advanced Microwave's circular waveguides, available in sizes ranging from WR10 to WR2300, provide the precision needed for these demanding applications. When satellite ground stations transmit and receive signals, every decibel of signal preservation matters, making the lower attenuation characteristics of circular waveguides invaluable. These waveguides maintain signal integrity across the broad frequency ranges required for diverse satellite services, whether for television broadcasting, internet connectivity, or military communications. The robust construction of Advanced Microwave's circular waveguides also provides the durability needed for outdoor satellite equipment that must withstand harsh environmental conditions including temperature extremes, precipitation, and solar radiation. Additionally, circular waveguides simplify the implementation of rotary joints in tracking antennas, which need to maintain consistent electrical properties while constantly repositioning to follow satellites in orbit. This mechanical advantage significantly improves system reliability in mission-critical applications. The broad frequency range covered by Advanced Microwave's circular waveguides (1 GHz to 110 GHz) ensures compatibility with virtually all satellite communication bands from L-band through Ka-band and beyond, making them versatile components in complex communication networks where multiple frequency bands must be accommodated.
Radar and Defense Applications
In radar and defense systems, the structural advantages of Circular Straight Waveguide designs provide critical performance benefits that directly impact operational capabilities. Circular waveguides excel in high-power radar applications because their geometry distributes electromagnetic fields more evenly, preventing voltage breakdown that can occur at the corners of rectangular waveguides. This is particularly important in modern defense systems where power requirements continue to increase. Advanced Microwave's circular waveguides, manufactured to ISO:9001:2008 standards and fully RoHS compliant, deliver the precision and reliability demanded by military specifications. The superior mechanical strength of circular waveguides makes them ideal for shipboard and airborne radar systems where equipment must withstand significant vibration, shock, and movement. Their symmetrical design also simplifies the implementation of rotating radar assemblies while maintaining consistent electrical performance throughout rotation. Additionally, circular waveguides provide better performance in pressurized airborne systems where maintaining internal pressure is critical for preventing corona discharge at high altitudes. The circular geometry creates natural pressure vessels that resist deformation under pressure differentials. For phased array radar systems, which require precise phase relationships between elements, the consistent electrical properties of circular waveguides ensure accurate beamforming and target tracking. Advanced Microwave's standard circular waveguide sizes such as WR28C, WR42C, WR75C, and WR90C provide options for various radar bands from X-band through Ka-band, covering most military radar applications. The lower signal distortion characteristics of Circular Straight Waveguide components translate directly to improved detection ranges and target discrimination capabilities in sophisticated defense systems where performance margins can determine mission success.
Scientific Research and Testing Facilities
Research institutions and testing facilities leverage the unique structural advantages of Circular Straight Waveguide technology to achieve precise, repeatable electromagnetic measurements and experimental setups. The uniform field distribution within circular waveguides provides researchers with more predictable and mathematically elegant wave propagation models, simplifying theoretical analysis and experimental comparison. Advanced Microwave's circular waveguides, with their highly controlled manufacturing tolerances, support the exacting standards required for scientific research. Particle accelerators and high-energy physics facilities often utilize circular waveguides for RF power delivery because of their superior power handling capabilities and lower losses. When experiments require kilowatts or even megawatts of microwave power, the structural integrity of circular waveguides prevents deformation and maintains consistent performance under thermal stress. Additionally, scientific metrology labs benefit from the rotational symmetry of circular waveguides when developing calibration standards and reference materials for microwave measurements. The aluminum, copper, or brass construction options offered by Advanced Microwave allow researchers to select materials optimized for their specific experimental requirements, whether prioritizing conductivity, weight, or thermal stability. Circular waveguides also provide advantages in plasma physics research where high-power microwaves are used to heat plasmas for fusion energy experiments. Their higher power thresholds and breakdown resistance make them ideal for these extreme applications. Advanced Microwave's laboratories, equipped with measurement capabilities up to 110 GHz, ensure that researchers receive circular waveguide components with fully characterized performance parameters, essential for experimental validity and reproducibility. For research involving specialized propagation modes or novel electromagnetic phenomena, the well-defined mode structure in Circular Straight Waveguide systems provides a controlled environment that minimizes unwanted mode conversion or coupling effects that could contaminate experimental results.
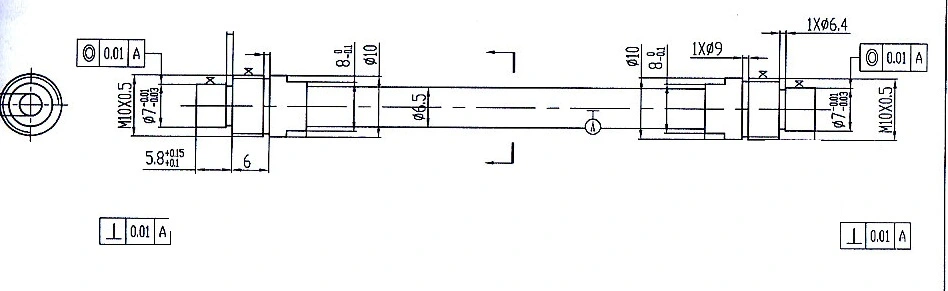
Manufacturing and Design Considerations
Material Selection and Surface Treatment
The material composition and surface treatment of Circular Straight Waveguide products significantly impact their performance and directly leverage their structural advantages. Advanced Microwave carefully selects materials based on application requirements, offering circular waveguides in aluminum, copper, or brass to optimize conductivity, weight, and cost parameters. Aluminum waveguides provide excellent weight-to-performance ratios crucial for aerospace applications, while copper offers superior conductivity for lowest-loss requirements, and brass delivers a balance of machinability and performance. The circular geometry presents unique opportunities for surface treatment that rectangular waveguides cannot match. The absence of corners allows for more uniform electroplating processes, resulting in more consistent conductivity across the waveguide's interior surface. Advanced Microwave's conductive gold or silver plating options enhance the already superior attenuation characteristics of circular waveguides. This plating process is particularly critical for Circular Straight Waveguide performance as it directly impacts skin effect losses at higher frequencies. The uniform circular cross-section facilitates more consistent plating thickness compared to rectangular waveguides where corners often receive less plating material. Additionally, the circular interior allows for more effective post-manufacturing cleaning and inspection processes, ensuring removal of any contaminants that could degrade electrical performance. Surface roughness, which directly impacts attenuation through increased skin effect losses, can be more precisely controlled during manufacturing of circular waveguides. Advanced Microwave's strict quality control procedures ensure surface finish meets exacting standards, maintaining the theoretical advantages of circular waveguide geometry in practical implementations. For specialized applications requiring exceptional performance, Advanced Microwave can implement enhanced surface treatments such as specialized polishing techniques or advanced plating materials that would be difficult to apply uniformly in rectangular waveguide geometries, further extending the inherent advantages of circular structures.
Precision Manufacturing Techniques
The production of high-performance Circular Straight Waveguide components requires specialized manufacturing techniques that preserve their inherent structural advantages. Advanced Microwave employs precision machining and forming processes optimized specifically for circular geometries to maintain the strict dimensional tolerances required for predictable electromagnetic performance. Unlike rectangular waveguides where dimensional variations primarily affect cutoff frequencies, circular waveguides are more sensitive to concentricity and roundness errors that can disrupt mode propagation. Advanced Microwave's manufacturing processes focus on maintaining these critical parameters. Their ISO:9001:2008 certified production facilities implement rigorous quality control protocols that include specialized measurement techniques for verifying circular waveguide dimensions and surface quality. The manufacturing of Circular Straight Waveguide products involves precision boring or drawing operations that create the exact inner diameter critical for maintaining the waveguide's specified operating frequency range. Advanced Microwave's capabilities span waveguide sizes from WR10 to WR2300, requiring exceptional manufacturing flexibility and precision. The flange integration process for circular waveguides presents unique challenges compared to rectangular versions. Advanced Microwave has developed specialized techniques for attaching CPR, UBR, or custom-designed flanges to circular waveguides while maintaining precise alignment and electrical continuity. This ensures that the VSWR remains at or below 1.20:1 as specified. Advanced Microwave's technical R&D team continuously refines manufacturing processes to address the special requirements of circular waveguides, implementing innovations that maintain tight tolerances while improving production efficiency. This focus on manufacturing excellence ensures that the theoretical advantages of circular waveguide geometries are fully realized in finished products. Additionally, their fast prototyping capabilities allow for rapid iteration and optimization of custom designs, enabling clients to quickly validate the performance benefits of Circular Straight Waveguide solutions for their specific applications before committing to full production runs.
Customization and Integration Solutions
The unique structural advantages of Circular Straight Waveguide designs create special opportunities for customization and system integration that Advanced Microwave expertly leverages for client-specific requirements. The inherent symmetry of circular waveguides simplifies the design of rotary joints and other specialized components that would be considerably more complex with rectangular waveguides. Advanced Microwave's OEM services capitalize on this advantage to create integrated solutions for moving antenna systems and other dynamic applications. For clients with non-standard frequency requirements, the circular geometry offers more flexible cutoff frequency adjustment through precise diameter control compared to rectangular waveguides where two dimensions must be coordinated. Advanced Microwave's engineering team utilizes sophisticated electromagnetic simulation tools to optimize custom Circular Straight Waveguide designs that maximize performance for specific operational parameters. When systems require transitions between circular and rectangular waveguides, Advanced Microwave provides carefully engineered components that minimize reflection and mode conversion losses at these critical junctions. Their technical expertise ensures that the inherent advantages of circular waveguides are preserved even when integrating with other transmission line technologies. The adaptability of circular waveguides to various flange types enables seamless integration with existing infrastructure. Advanced Microwave offers CPR, UBR, or entirely custom-designed flanges to match specific system requirements while maintaining the electrical advantages of the circular waveguide structure. For applications requiring specialized surface properties or environmental protection, Advanced Microwave can implement custom coating processes beyond standard gold or silver plating, including specialized treatments for extreme temperature environments or corrosive conditions. Their professional technical R&D team works closely with clients to develop Circular Straight Waveguide solutions that address unique challenges while maintaining strict performance specifications. The company's integrated production and R&D capabilities allow for continuous refinement of designs based on real-world testing and feedback, ensuring that custom circular waveguide solutions meet or exceed performance expectations even in the most demanding applications.
Conclusion
Circular Straight Waveguides offer compelling structural advantages over rectangular alternatives, including superior mode propagation, enhanced mechanical strength, and lower high-frequency attenuation. These benefits make them invaluable across telecommunications, defense, and scientific research applications. Advanced Microwave Technologies Co., Ltd. leverages these advantages through precision manufacturing and customization capabilities, delivering high-performance waveguide solutions tailored to specific requirements. For projects requiring optimal signal integrity and mechanical reliability, our extensive expertise in circular waveguide technology ensures exceptional results. Contact our engineering team at sales@admicrowave.com to discover how our circular waveguide solutions can enhance your next project with our perfect supply chain system, fast delivery, and unmatched quality control.
References
1. Johnson, R.C. & Jasik, H. (2021). "Antenna Engineering Handbook: Waveguide Theory and Applications," 5th Edition. McGraw-Hill Professional.
2. Zhang, L. & Wu, K. (2023). "Comparative Analysis of Circular and Rectangular Waveguides for Millimeter-Wave Applications." IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 71(3), 1297-1312.
3. Pozar, D.M. (2022). "Microwave Engineering," 5th Edition. John Wiley & Sons.
4. Chen, X., et al. (2024). "Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Precision Circular Waveguides in Satellite Communication Systems." Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 38(4), 456-470.
5. Williams, D.F. & Rogers, J.E. (2023). "Structural Integrity and Electromagnetic Performance of Waveguides Under Environmental Stress." International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering, 33(1), 78-94.
6. Ahmadi, S. & Ghannouchi, F.M. (2021). "Analysis of Power Handling Capabilities in Circular vs. Rectangular Waveguide Structures." IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 31(5), 522-524.
YOU MAY LIKE
 VIEW MOREEnd Launch Waveguide to Coaxial Adapter
VIEW MOREEnd Launch Waveguide to Coaxial Adapter VIEW MORECircular Straight Waveguide
VIEW MORECircular Straight Waveguide VIEW MOREInflatable Straight Waveguide
VIEW MOREInflatable Straight Waveguide VIEW MORECircular Waveguide Transition
VIEW MORECircular Waveguide Transition VIEW MOREFlexible Twistable Waveguide
VIEW MOREFlexible Twistable Waveguide VIEW MOREFlexible Seamless Waveguide
VIEW MOREFlexible Seamless Waveguide VIEW MORERight Angle Waveguide To Coaxial Adapter
VIEW MORERight Angle Waveguide To Coaxial Adapter VIEW MORECircular Waveguide To Coaxial Adapter
VIEW MORECircular Waveguide To Coaxial Adapter




